
Electrochemical Sensor for Real-Time Detection of Antipsychotic Clozapine
2University of Maryland, USA
Background: Clozapine is the most effective antipsychotic medication for schizophrenia; yet, clozapine is underutilized due to burdensome treatment monitoring schemes and adverse side effects. Electrochemical sensors can be used to measure clozapine, however, their performance dramatically decrease in biofluids due to the presence of interfering redox-active active molecules. Our project is focused on developing an electronic tongue-based micro-sensor, which comprises an array of microelectrodes modified with different films to induce different selectivities. The complex electrochemical signals generated from the sample are analyzed using chemometric algorithms. Here, we present the development of an array of microelectrodes modified with electrocatalytic modifications that will be used to enable a minimally invasive, real-time and in-situ monitoring of clozapine levels in a finger-pricked volume of a whole blood sample.
Methods: We modified microfabricated microelectrodes (Fig.1A) with reduced graphene oxide film (r-GO; Fig.1B) and chitosan-carbon nanotubes (chitosan-CNT; Fig.1C) bio-composite using electrodeposition techniques. The r-GO–modified microelectrode allows highly repeatable sensing and chitosan-CNT –modified microelectrode allows highly sensitive detection of clozapine in biofluids.
Results: Following optimization of the r-GO and the chitosan-CNT modifications, we demonstrated the proof-of-concept detection of clozapine by using each of the modified electrode separately in a 20µL volume sample of spiked whole blood (Fig.1D). From the dose response characteristics plot, we measured a limit-of-detection of 0.60±0.04µM and 0.50±0.06μM and a sensitivity of 6.3±0.3A/cm2M and 7.5±0.4A/cm2M using the r-GO and chitosan-CNT –modified microelectrodes, respectively (Figs.1E&1F).
Conclusion: We demonstrated the ability to detect the levels of clozapine below the clinical threshold (1-3µM).
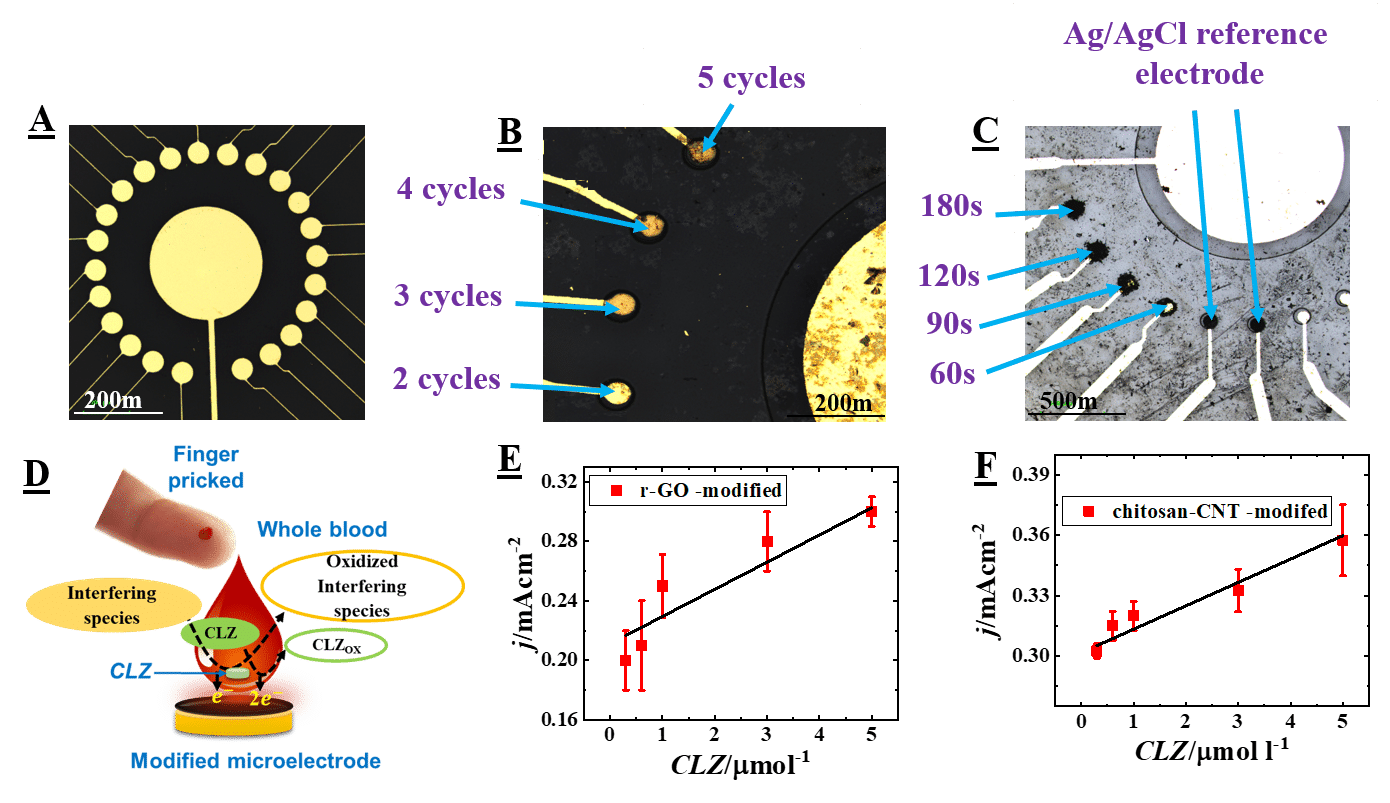
Figure. 1. (A) Microfabricated arrayed chip (B) Different number of cycle-based r-GO –modified gold microelectrode(C) on chip Ag/AgCl reference microelectrode and different time duration based chitosan-CNT –modified gold microelectrode (D) Scheme of clozapine detection in finger-pricked microliter volume of spiked whole blood. Clozapine dose response characteristics measured by using (E) the r-GO –modified and (F) the chitosan-CNT –modified microelectrode
Powered by Eventact EMS