
Experimental Therapy for Bone Metastatic Prostate Cancer with MicroRNA145 Inhibits Tumor Growth In Vivo
The metastatic prostate cancer presents unfavorable, without cure and with high comorbid and low quality of life. Micro RNA (miRNA) is a class of non-coding RNA responsible for the expression control of at least 30% of human genes. Here we presents the effects of treatment with miRNAs 145 in a pre-clinical model of disseminated bone metastatic prostate cancer.
Methods
The pre-clinical model was created by the intra-cardiac injection of the cell line containing luciferase gene PC3-Luc-C6 in nude mice (Balb/c). Tumor growth was evaluated with in vivo bioluminescence (IVIS). After the full establishment of the bone metastasis at day 21 we treated the animals with three tail vein injections. They were analyzed weekly until day 48.
Results
The model of bone metastatic prostate cancer was well stablished with diffuse metastasis on day 21. We treated the animal intravenously with the microRNA conjugated with atelocollagen on days 21, 24 and 27. Immediately after the beginning of the treatment the tumor stopped growing reaching a statistical difference one week after the third dose when compared with the negative control. After this transitory tumor suppressor effect, the tumors returned to growth again (Figure).
Conclusion
In animals with diffuse metastatic disease, the treatment with mir145 leads to consistent but temporally response due to a fast degradation of these microRNAs and to cancer cells mechanisms of scape and resistance. Further studies with this purpose and design will permit the development of novel target drugs based on microRNAs for suppress the metastatic prostate cancer growth.
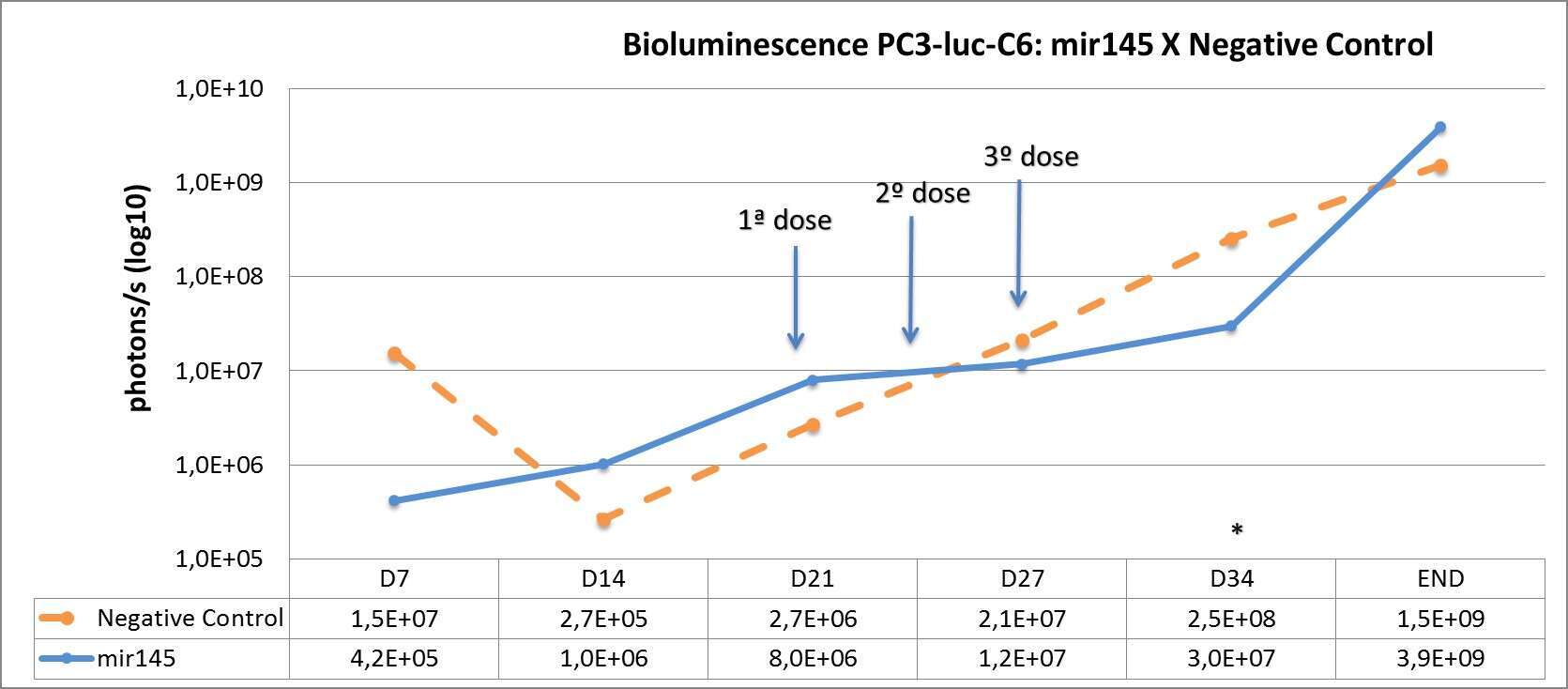
Figure. Average bioluminescence in both groups, mir145 (n=8) and negative control (n=4). On day 34 the difference was significant (p=0,04)
Powered by Eventact EMS