
THE STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR THE SPECIFICITY OF ABP, A GH27 ARABINOPYRANOSIDASE FROM GEOBACILLUS STEAROTHERMOPHILUS
2Department of Biotechnology and Food Engineering, Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa
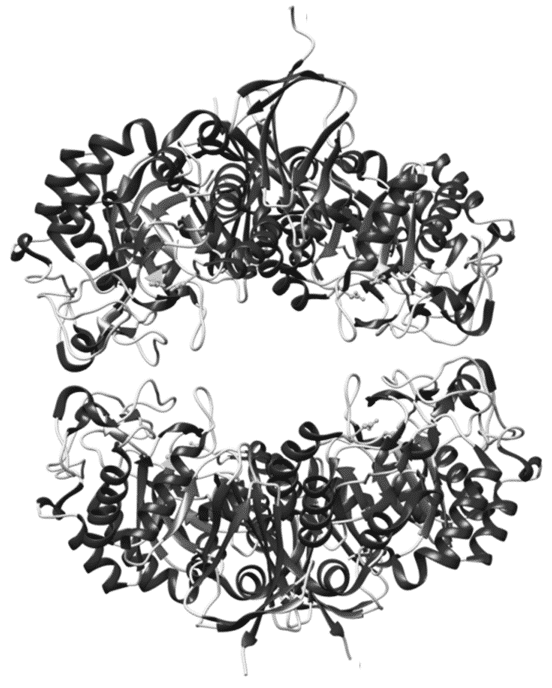
Geobacillus stearothermophilus T-6 is a Gram-positive thermophilic soil bacterium that has a highly-regulated hemicellulolytic system for the utilization of L-arabinan. This system includes a large array of proteins, which are involved in the sensing, uptake, degradation and metabolism of arabinan. A key protein involved in this degradation system is Abp, an intracellular GH27 β-L-arabinopyranosidase, which removes arabino-pyranose units from decorated arabino-oligosaccharides. To determine the structural basis for the observed specificity of Abp, we investigated and report here the X-ray crystal structures of Abp-WT and one of its catalytic mutants in complex with an arabinose reaction product [1,2]. The monomeric structure of Abp consists of two domains typical to GH27 enzymes, an N-terminal TIM-barrel domain and a C-terminal all-β domain. Unlike many GH27 enzymes, however, the quaternary structure of Abp is tetrameric, resembling two "open-pincer" dimers clamped around a central cavity (Figure). The biological relevance of this assembly is supported by gel-filtration, DLS and SAXS experiments. The conformations of the arabinose molecules trapped in the active sites hint at the different conformational changes that the b-L-arabinose molecule undergoes while being cleaved from the polysaccharide substrate by Abp. Finally, the Abp structure and kinetic Abp-mutant measurements reveal that a single isoleucine residue (Ile67), located at a key position in the active site, plays a critical role in the substrate specificity of the enzyme, contributing to the high preference of Abp toward arabinopyranoside over galactopyranoside substrates.
[1] S. Lansky, R. Salama, H.V. Solomon, H. Belrhali, Y. Shoham, G. Shoham, Acta Crystallogr. F 2013, 69, 695–699.
[2] S. Lansky, R. Salama, H.V. Solomon, H. Feinberg, H. Belrhali, Y. Shoham, G. Shoham, Acta Crystallogr. D 2014, 70, 2994–3012.
Powered by Eventact EMS