
NANOPARTICLE METALLIZATION OF FLEXIBLE CONDUCTING POLYMER ELECTRODE
2Department of Physical Electronics, School of Electrical Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv
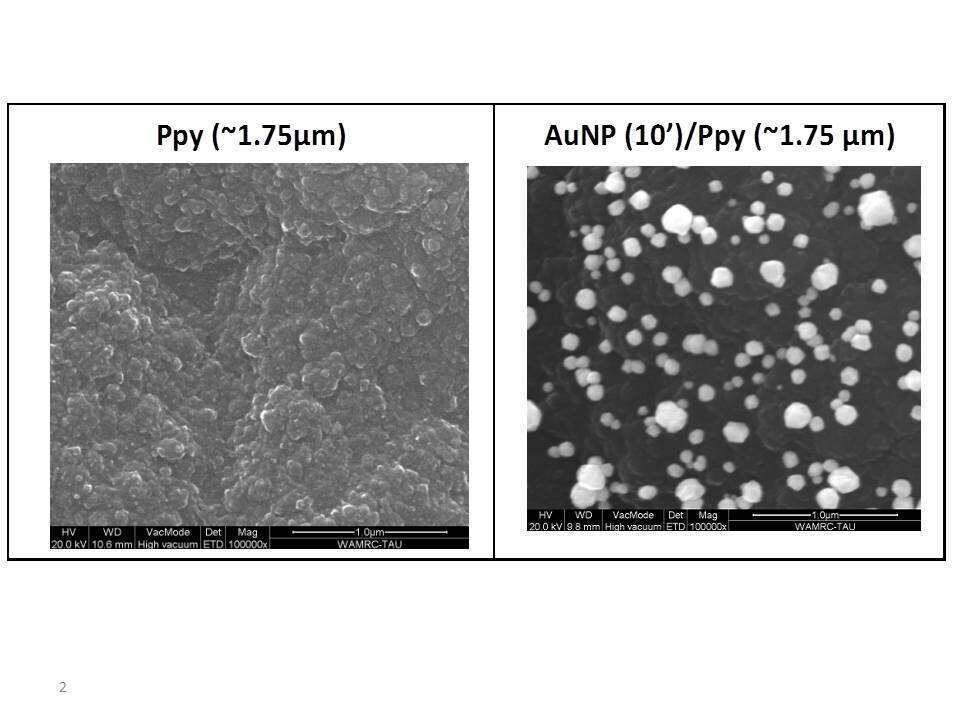
Flexible electrodes made of conjugate polymers are used for whole plastic MEMS & bio-electrochemical sensors. In this study we report on novel electrode made of metal nanoparticle on conductive polymers. Gold was electroplated on polypyrrole, and Platinum nanoparticles were deposited on polyaniline using Cluster Deposition.
One application for the conjugate polymer conductor was electrodes for “All polymer” MEMS. Another application is bio-electrochemical sensing of redox reactions, for example for detecting electrochemically active products of enzymatic reactions. In this research, the device fabrication process flow is described as well as its electrical properties. The polymers (polypyrrole and polyaniline) were deposited by electrochemical polymerization and metal nanoparticles were deposited by one of two methods: gold was deposited on polypyrrole by electroplating, and platinum nanoparticles were deposited on polyaniline using Cluster Deposition. The metal nano-particle layers were less than one nano-particle monolayer thick which maintained the device flexibility while its electrochemical behavior was similar to that of bare gold electrode.
The new electrode demonstrated a comparable sensing of enzymatic activity to that of planar gold electrode, as opposed via amperometric detection. Thus, this new electrode can serve as a highly sensitive, high surface area and flexible sensor for biological species.
Powered by Eventact EMS