
BENCHMARK AB INITIO CONFORMATIONAL ENERGIES FOR THE PROTEINOGENIC AMINO ACIDS THROUGH EXPLICITLY CORRELATED METHODS. ASSESSMENT OF DENSITY FUNCTIONAL METHODS.
2School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, The University of Western Australia
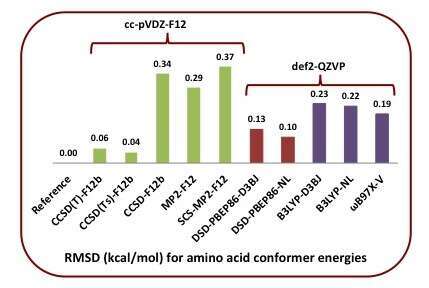
The relative energies of the YMPJ conformer database of the twenty proteinogenic amino acids, with N- and C-termination, have been re-evaluated using explicitly correlated coupled cluster methods. Lower-cost ab initio methods such as MP2-F12 and CCSD-F12b actually perform less well than double-hybrid DFT functionals: in particular, the DSD-PBEP86-NL double hybrid performs well enough to serve as a secondary standard. Among range-separated hybrids, ωB97X-V performs well, while B3LYP-D3BJ does surprisingly well among traditional DFT functionals. Treatment of dispersion is important for the DFT functionals: for the YMPJ set, D3BJ generally performs as well as the NL nonlocal dispersion functional. Basis set sensitivity for DFT calculation on these conformers is weak enough that def2-TZVP is generally adequate. For conformer corrections to heats of formation, B3LYP-D3BJ and especially DSD-PBEP86-D3BJ or DSD-PBEP86-NL are adequate for all but the most exacting applications. The revised geometries and energetics for the YMPJ database have been made available as electronic supporting information and should be useful in the parametrization and validation of molecular mechanics force fields and other low-cost methods. The very recent dRPA75 methods yields good performance, without resorting to an empirical dispersion correction, but is still outperformed by DSD-PBEP86-D3BJ and particularly DSD-PBEP86-NL.
Powered by Eventact EMS