
BH4− PROMOTED, RADICAL INITIATED, CATALYTIC OXIDATION OF (CH3)2SO BY N2O IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS
2Department of Chemistry, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev
3Biological Chemistry, Ariel University
The radiolysis of (CH3)2SO in N2O saturated aqueous solutions yields CH4 and C2H6 via the following reactions:
- (CH3)2SO + OH· → (CH3)2S·(O)OH → ·CH3 + CH3S(O)OH
- ·CH3 + (CH3)2SO → CH4 + ·CH2(CH3)SO
- 2·CH3 → C2H6
with a yield of G(CH4) + 2G(C2H6) = 6.0.
Surprisingly when NaBH4 is added to the solution G(CH4) + 2G(C2H6) > 100 is obtained, indicating that a chain reaction occurs. This result indicates that under these conditions the following catalytic process occurs:
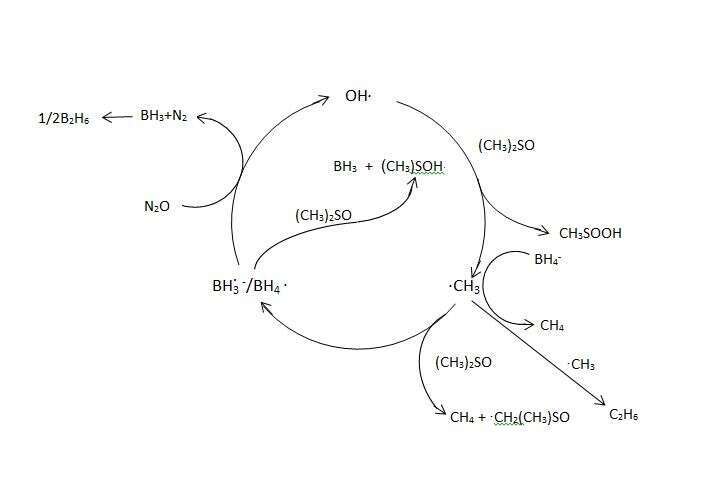
The reaction: BH4. + N2O → N2 + BH3 + OH· was previously reported [1].
4. OH. + BH4− → BH4. + OH−
The effects of [(CH3)2SO] and of the dose rate were studied. The results point out that N2O saturated solutions in the presence of BH4- can be used to catalytically hydroxylate various organic compounds.
Literature:
[1] Baxendale, J.H.; Breccia, A.; Ward, M.D.; Brown, J., Int. J. Radiat. Phys. Chem., 1970, 2, 167-176.
Powered by Eventact EMS