
NOVEL SYNTHESIS OF DEUTEROSILANES VIA RADICAL H/D EXCHANGE MEDIATED BY Pt(0) COMPLEXES. FIRST EPR OBSERVATION OF A PLATINUM (I) CENTERED RADICAL
The rising interest in deuterium-labeled compounds stimulates the search for selective and catalytic methods for their preparation. Silanes are very useful reagents in synthesis and are environmentally friendly reductants alternatives to metallo-based or toxic tin derivatives, because of their tolerance to air, moisture and low toxicity. Despite these advantages, the use of deuterated silanes as isotopic labeling reagents is very limited, most probably due to the limited number of methods for their synthesis.
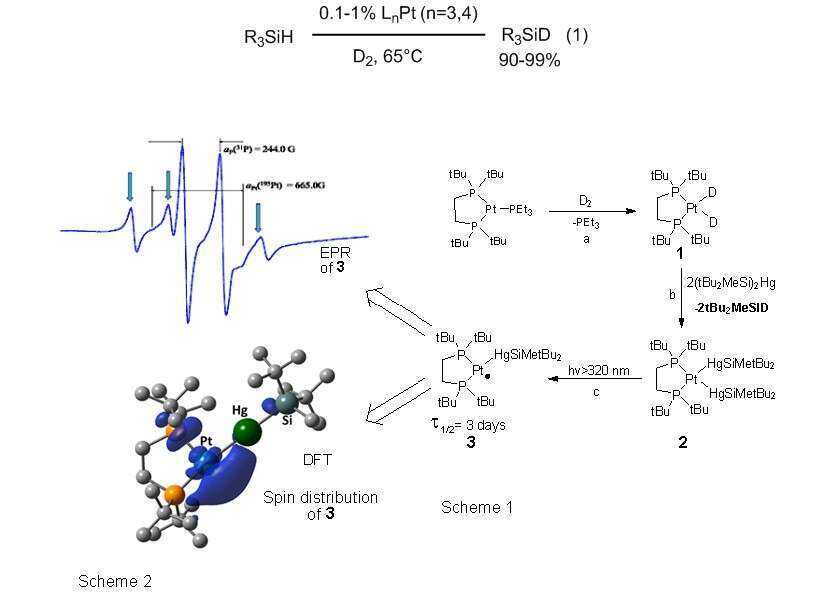
We report that phosphino-platinum(0) complexes activate Si-H and D-D bonds catalyzing the deuteration of different silanes in good yields under mild conditions (Eq. 1). We present evidence that the catalysis is mediated by a platinum di-deuteride intermediates e.g. 1 (Scheme 1, step a) and proceeds via homolytic activation of Si-H and Pt-D bonds. This is supported by isolation of trapping products of the corresponding platinum and silyl radicals with TEMPO ((2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidin-1-yl)oxyl) and the enhancing effect of AIBN (azobisisobutyronitrile) on the reaction yields. Furthermore, we demonstrate that Pt(I) complexes are viable species. Thus, we prepared from 1 a novel PtHg2 complex 2 (Scheme 1, step b), which upon irradiation yields 3 (Scheme 1, step c) - the first Pt(I) paramagnetic species which was characterized by EPR spectroscopy and DFT calculations (Scheme 2).
Powered by Eventact EMS