
A New CARTO® Segmentation Module Software to Facilitate Ablation of Arrhythmias
Introduction: We describe the use of the new CARTO® Segmentation Module Software (Biosense Webster) in VT ablations. The new module allows pre-procedural identification and three dimensional (3-D) reconstructions with high (≈ 1 mm) spatial resolution of all heart chambers including the aortic root, coronary arteries and coronary sinus (CS) based on cardiac CT.
Methods: All 10 consecutive patients (pts) who underwent VT ablation using the new software between 08-11/2015 were included. Registering the CT image into the CARTO® navigation system was done rapidly by using the non-coronary cusp (NCC) as a landmark and FAM the aortic volume with the ablation catheter.
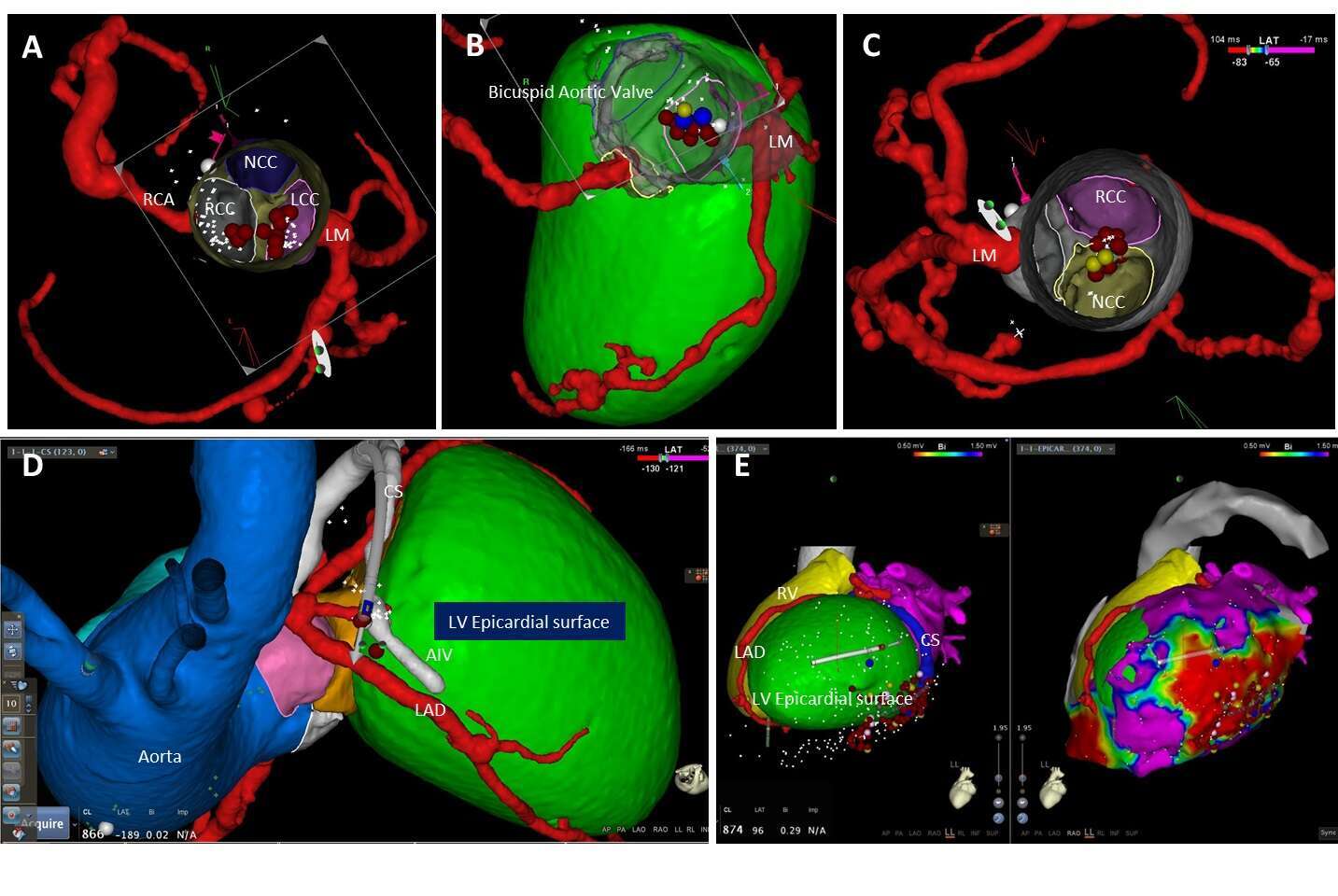
Results: Eight pts underwent outflow tract arrhythmia ablation and 2 pts ischemic VT ablation. The junction of the right coronary cusp (RCC) - left coronary cusp (LCC) commissures was the most common arrhythmia site of origin (SOO) (3 pts)(Fig. A). Other locations included: LCC, the junction of the RCC-NCC (Fig. C), the aortic-mitral continuity, midseptal RVOT and a CS branch. Acute successful ablation was achieved in 6 pts with transient arrhythmia abolition in 7 pts. The procedure was discontinued in 2 pts due to close proximity of the coronary arteries to the arrhythmia SOO (Fig. B,D). The ischemic VT ablations were endocardial in combination with epicardial (Fig. E). No complication occurred in any of the patients.
Conclusion: The CARTO® Segmentation Module assists in accurately identifying the exact anatomic location during ablation procedures, in safely ablating in close proximity to the coronary arteries, abetting successful ablation.
Powered by Eventact EMS