
THE UTILIZATION OF METAL NANOPARTICLES FOR STUDYING THE CATALYTIC WATER REDUCTION MECHANISM BY SODIUM BOROHYDRIDE USING ISOTOPIC MARKERS
Nanocatalysts and in particular metal nanocatalysts are one of the most exciting subfields emerged from the nanoscience. Nanoparticles (NPs) are known for their remarkable catalytic abilities and they are extensively investigated due to their properties. Furthermore, water reduction is a reaction vastly studied. There are many studies engaged in catalytic water reduction by sodium borohydride but the mechanism of these reactions is still unknown.
We are investigating the catalytic water reduction by metal NPs catalysts (silver: Ag-NPs, gold: Au-NPs and platinum: Pt-NPs) usingsodium borodeuteride (NaBD4) as an isotopic marker. We monitored the reactions using mass-spectrometry (MS) by following the masses at 2, 3 and 4 amu corresponding to H2, HD and D2, respectively. From the ratios between these products one can conclude about the reduction mechanism.
The reported results indicate that:
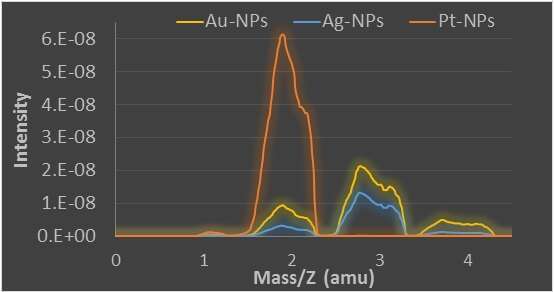
- Ag-NPS and Au-NPs have similar catalytic properties which are time-depended.
- Pt-NPs catalyze water reduction similarly to Ag-NPS and Au-NPs, but all of the gaseous products are converted to H2 due to an efficient equilibrium between adsorbed dihydrogen and protons in solution.
Powered by Eventact EMS