
INTRACAVITY LASER ABSORPTION SPECTROSCOPY FOR COMBUSTION DIAGNOSTICS
2Department of Natural Sciences, The Open University of Israel
3Division of Combustion Physics, Lund University
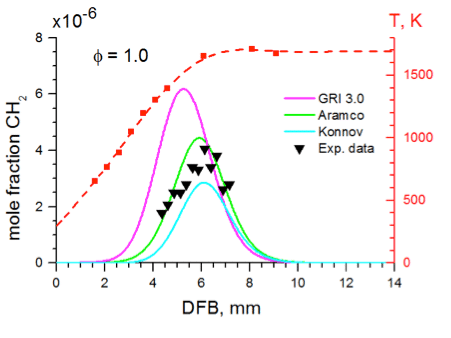
Laser-based diagnostic measurements provide a rigorous test of our understanding of combustion chemistry. Intracavity Laser Absorption Spectroscopy (ICLAS) technique used for absolute concentration measurements of HCO and 1CH2 radicals, playing an important role in combustion mechanism.
The experimental spectra of the HCO and CH2 radicals were recorded for different equivalence ratios. The interpretation of the spectral data is presented and its potential for the combustion model development is discussed. (see Fig.1)
 New methodology for concentration measurements of CO, CO2, CH4, and H2O and thermometry based on broadband detection of these species, using Fiber Laser Intracavity Absorption Spectroscopy (FLICAS) was developed and verified. The experiments were performed in a temperature-controlled flow-cell, which allowed evaluating the feasibility of the FLICAS technique for temperature and concentration diagnostics.
New methodology for concentration measurements of CO, CO2, CH4, and H2O and thermometry based on broadband detection of these species, using Fiber Laser Intracavity Absorption Spectroscopy (FLICAS) was developed and verified. The experiments were performed in a temperature-controlled flow-cell, which allowed evaluating the feasibility of the FLICAS technique for temperature and concentration diagnostics.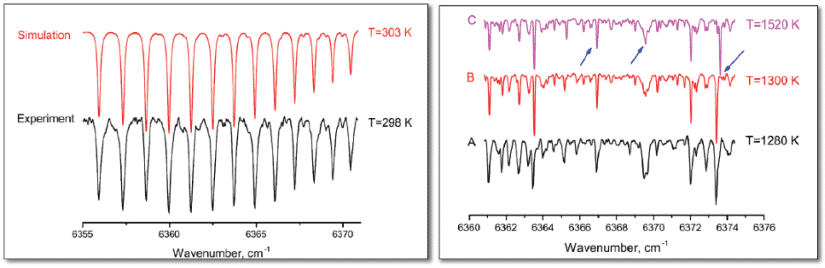
We have found that CO and CO2 spectra are well described by HITRAN database allowing for accurate and simultaneous determination of temperature and concentration. Our study demonstrates that for CH4 and H2O the deficiencies of HITRAN database (especially for high temperature conditions) somewhat limit the use of these molecules as candidates for thermometry in combustion related devices. (see Fig.2)
Powered by Eventact EMS