
SYNTHESIS AND EVALUATION OF GIBBERELLIC ACID BASED PHOTOACTIVE CHEMICAL PROTEOMICS TOOLS
2Department of Molecular Biology and Ecology of Plants, Tel-Aviv University
Gibberellins are plant hormones that control diverse aspects of growth and development in plants.1 The major bioactive gibberellins (GAs), which include GA1, GA3, GA4 and GA7, are derived from a basic diterpenoid carboxylic acid skeleton, and commonly have a C3-hydroxyl group. We have developed an efficient synthesis that allows access to gibberellic acid (GA3) photo-affinity probes (Fig. 1) from readily available starting materials. The probes contain a photoreactive group, a diazirine moiety, and a handle which will allow us to perform biorthogonal chemistry2 in order to pull down potential proteins that bind the bioactive gibberellins. We tested these GA3 probes in Arabidopsis thaliana and the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. These probes promote GFP-RGA degradation in planta and rescue root elongation in paclo-treated plants in Arabidopsis. Probe 3 showed a significant agonist effect on the quorum sensing of A. tumefaciens. Based on these preliminary results we set out to identify unknown proteins that interact with gibberellins in these two organisms.
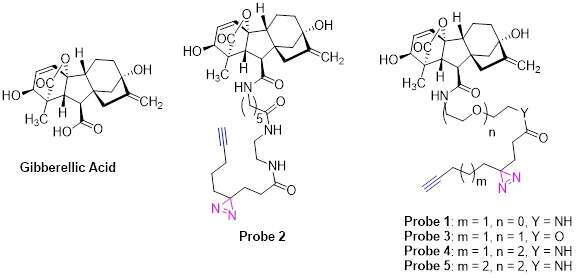
Fig 1. Chemical structures of gibberellic acid (GA3) and probes (1-5).
References
- Yamaguchi, S., Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 225–251.
- (a) Amara, N.; Mashiach, R.; Amar, D.; Krief, P.; Spieser, S. p. A. H.; Bottomley, M. J.; Aharoni, A.; Meijler, M. M., J Am Chem Soc 2009, 131, 10610-10619; (b) Dubinsky, L.; Delago, A.; Amara, N.; Krief, P.; Rayo, J.; Zor, T.; Kravchenko, V. V.; Meijler, M. M., Chem Commun 2013, 49, 5826-5828; (c) Dubinsky, L.; Jarosz, L. M.; Amara, N.; Krief, P.; Kravchenko, V. V.; Krom, B. P.; Meijler, M. M., Chem Commun 2009, 47, 7378-7380; (d) Rayo, J.; Amara, N.; Krief, P.; Meijler, M. M., J Am Chem Soc 2011, 133, 7469-75.
Powered by Eventact EMS