
A Wireless Frequency Domain Beamforming Based Ultrasound Imaging
2The department of Electrical Engineering, The Technion, Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa
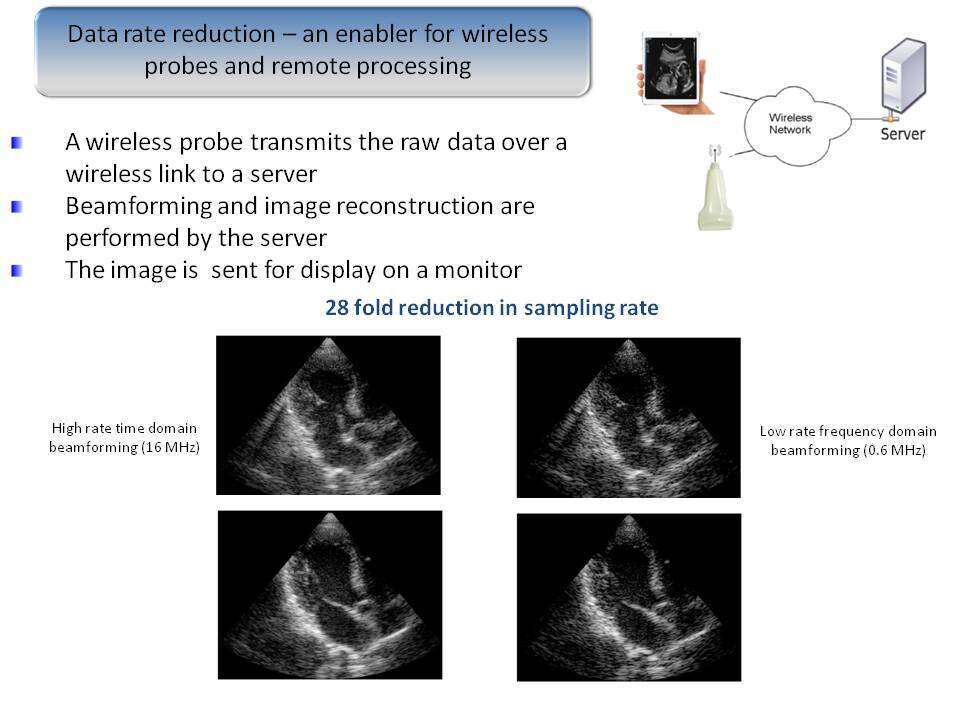 Background: Considerable reduction both in sampling rate and processing time can be achieved in ultrasound imaging by applying compressed sensing, Xampling and frequency domain beamforming, leading to sub-Nyquist sampling rates. This study evaluated this model to create a wireless ultrasound.
Background: Considerable reduction both in sampling rate and processing time can be achieved in ultrasound imaging by applying compressed sensing, Xampling and frequency domain beamforming, leading to sub-Nyquist sampling rates. This study evaluated this model to create a wireless ultrasound.
Methods: Ultrasonic signals were received by a commercial ultrasound system transducer and were amplified, sampled and transformed to the frequency domain by a hardware component referred to as a "Xampler". The low rate data output received from this component was transmitted over a 802.11n wireless link to a computer where frequency domain beamforming was implemented in C language, utilizing Intel`s Integrated Performance Primitives (IPP) library to enhance performance. The design was implemented partly in Verilog and partly in VHDL. Simulations and synthesis were performed with VCS-MX and Design Compiler of Synopsys respectively. The physical design was done using Cadence`s Encounter tool.
Results: Imaging results are shown in Figure 1. An image reconstructed at the remote site from 122 complex valued samples per scan line, transmitted over a wireless link, had a quality similar to an image obtained by a state of the art commercial ultrasound imaging system with 2048 real-valued samples per scan line. The saving of 244/2048 ≈ 1/8 in raw data rate has enabled the wireless operation.
Discussion: Xampling and frequency domain beamforming manage to reduce sampling considerably enabling significant data storage and transmission reduction. Further studies are needed to correlate this system with clinical data and pathologies.
Powered by Eventact EMS