
Clinical Value of Serum Procalcitonin in Diagnosis of Infection in Patients with Acute Myocardial Infarction
2Infectious Diseases Control Unit, Assaf-Harofeh Medical Center, Be'er Ya'akov
3Sackler School of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Ramat-Aviv
4Microbiological laboratory, Assaf-Harofeh Medical Center, Be'er Ya'akov
Background: A significant proportion of patients with acute myocardial infarction (AMI) also present with signs of Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) but the incidence of infection in this population is low. Thus, when AMI patients become febrile, a dilemma arises pertaining to the need for antibiotics prescription which in turn may lead to misuse of antibiotics.
Serum Procalcitonin (PCT) is known to be elevated in bacterial infections but was also reported to be elevated to a small extent in AMI patients. It is unknown whether PCT levels can be utilized to differentiate between AMI patients with and without bacterial infection.
Methods: In this study, serum PCT (VIDAS bioMérieux, France) was collected within 48-72 hours of presentation in patients presenting with AMI. Baseline characteristics, and clinical and bacteriological data were collected prospectively. Determination of SIRS and/or infection was adjudicated by two infectious disease experts. The sensitivity and specificity of PCT to diagnose infection was calculated.
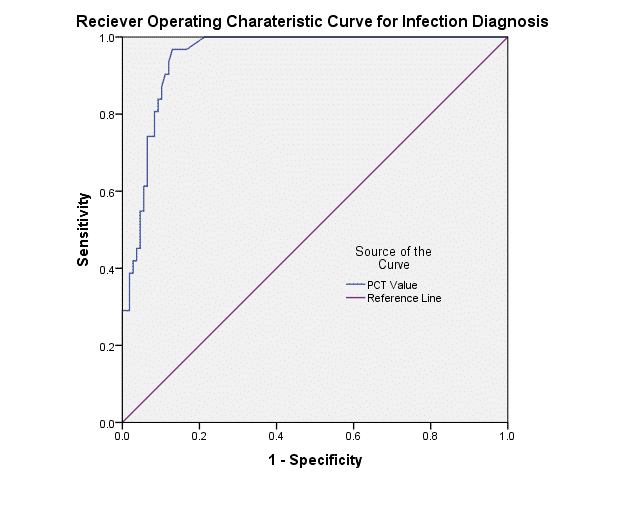
Results: Of 139 study patients (mean age 63.8±14.7 years), 31 (22.3%) had a final diagnosis of systemic infection and of them, 67.7% had elevated serum PCT (>0.5 ng/mL). The area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve (ROC-figure-1) for PCT, regardless of the cut-off value used, is 0.951. PCT level had a sensitivity of 67.74% and specificity of 93.52% for the diagnosis of systemic infection. When considering elevated serum PCT as a marker for severe infection/septic shock, the calculated sensitivity and specificity are 80.00% and 89.92 % respectively .When a cutoff of 0.2ng/mL is explored, the PCT test has sensitivity of 80.65% and specificity of 91.67% for infection and sensitivity of 85% and specificity of 85.7% for the diagnosis of severe infection.
Conclusions: PCT test is a highly specific marker for infection in AMI patients. Its utilization should be further explored in large scale studies.
Figure-1
Powered by Eventact EMS