
E/Z ISOMERIZATION OF STABLE SILENES
The photochemically promoted E⇌Z isomerization of alkenes is a very important class of reactions in chemical and biological processes and it has long been a subject of intense research. In contrast to alkenes, the chemistry of their silicon analogues, silenes (R2Si=CR2) and disilenes (R2Si=SiR2), is much less investigated.
In this work, we report the first stereospecific synthesis of two stable silenes (1) and study their photo-induced E⇌Z isomerization. 1 is obtained in a one-pot reaction of (tBuMe2Si)2(tBu2MeSi)SiLi with RC(=O)H in benzene at rt. Formation of 1 is stereospecific, giving the E-isomer (1a) as the main product. Upon irradiation with a 250 nm or 350nm UV lamp at rt, 1a isomerizes to the Z-isomer (1b), yielding at equilibrium a E:Z ratio of 51:49 for R=1-Ad and of 38:62 for R=Trip. The reaction can be thermally reversed. The kinetics of the thermal isomerization was measured and the activation energies as well as the energy differences between the E and Z isomers were experimentally obtained and compared to theoretical values. The mechanism of the Z to E isomerization was computationally investigated by DFT theory, and will be discussed.
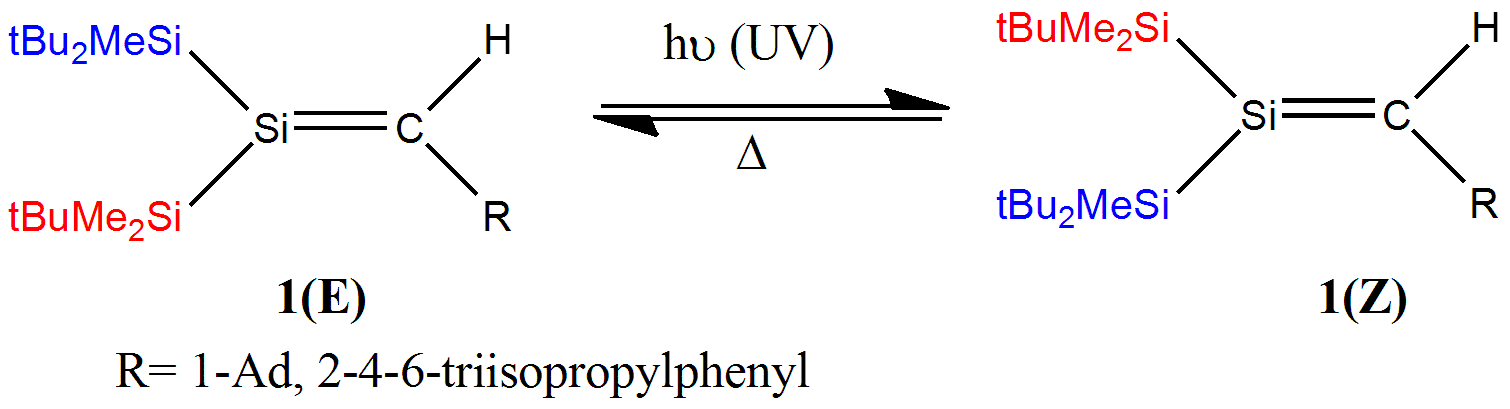
Powered by Eventact EMS