
Double Anti Platelet Therapy and Cytokine Status after Coronary Revascularization
AIMS
Evaluate the activity of markers of systemic inflammation (IL-1b, IL-6, IL-10) and platelet aggregation in patients with coronary artery disease undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
74 patients who had undergone during the last 2 years, coronary artery bypass grafting (n = 27) and stenting (n = 47) .median age 49-59 ,Underwent coronary artery bypass grafting 23 M and 4 W. Stenting was performed in 42 men and 5 women. The comparison group consisted of patients with chronic ischemic heart diseases .The study of platelet aggregation was carried out on a two-channel laser analyzer aggregation 230LA (NPF "Biola", Russia). As an inducer of aggregation using adenosine diphosphate (ADP) at a final concentration of 5.0 mM, 0.1 mM ADP, 1.0 mM ADP, 5.0 mM ADP (%).To determine the concentrations of cytokines (IL-1b, IL-6, IL-10) used a solid phase sandwich method with the appropriate reagent kit «Vector Best-Volga" (Nizhny Novgorod). Statistical processing of the results was carried out in the software package Statistica 8.0 (StatSoft Inc.).
Results
In the study higher atherogenic indices on higher levels of pro inflammatory cytokines in the blood of patients with stable angina .Simultaneously induced aggregation rates were significantly lower in patients after coronary revascularization, compared with patients receiving drug therapy alone.
Comparison of cytokine status in groups of patients after coronary revascularization in the background dual antiplatelet therapy and receiving only aspirin therapy showed significantly higher values of pro inflammatory cytokines in patients taking aspirin alone.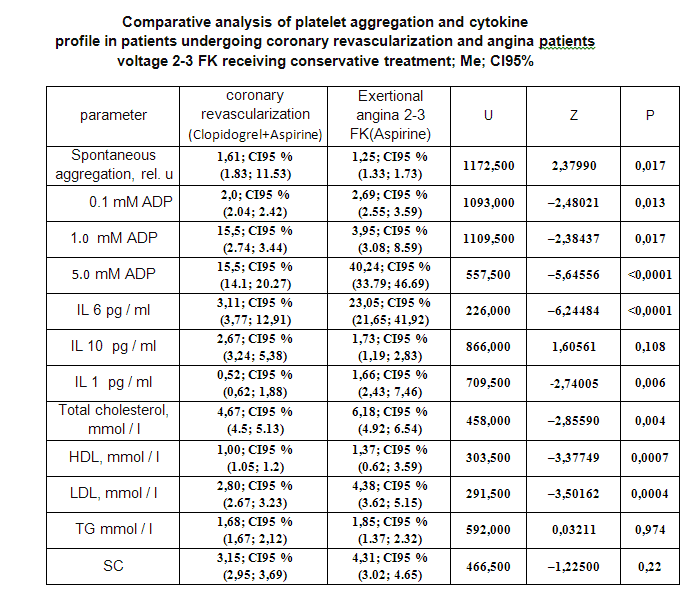
Powered by Eventact EMS