
The Diagnostic Value of Novamed’s Sens-A-Heart Rapid Assay in Patients
with Definite and Possible ACS
2Mount Scopus Internal Medicine, Hadassah-Hebrew University
3Department of Emergency Medicine, Mount Scopus
4., Novamed LTD
Background:
Sensitivity, specificity, and precision of the various commercially available troponin assays vary considerably. Sens-A-Heart is a novel rapid test using a combination of biomarkers, which provides a yes/no answer within 10 minutes using a single droplet of blood.
Aims:
The purpose of this study was to evaluate diagnostic accuracy of rapid Sens-A-Heart testing in patients with definite or possible ACS.
Methods:
The Sens-A-Heart test was performed in 120 consecutive patients with definite or possible ACS admitted to departments of Hadassah Medical Center (Jerusalem) between 01.09.2015 and 01.09.2016. Initial troponin evaluation and simultaneous Sens-A-Heart testing were done under the ESC and ACC consensus guidelines.
Results:
Final diagnosis of ACS was established in 75 patients (62.5%), nonischemic heart disease documented in 3 patients (2.5%) and noncardiac disease in 42 (35%) patients.
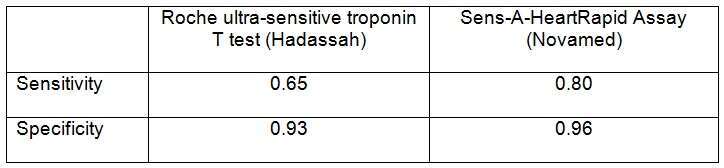
The Sens-A-Heart test was highly sensitive to coronary events - true positive predictive value in 80% of cases vs standard Hadassah troponin test which revealed 65% of cases.
The Sens-A-Heart test has also a high specificity for ACS - true negative rate was 96% vs 93% in Hadassah troponin test.
Conclusion:
Novamed’s Sens-A-Heart Rapid Assay has prominent diagnostic sensitivity and specificity in patients with ACS.
Powered by Eventact EMS