
Cobalt Catalyzed Aerobic Oxidative Cross Coupling of Phenols
Oxidative coupling reactions under aerobic condition are highly desired methods in organic chemistry; specifically the cross coupling of two phenolic components affording biphenol products, which are important for natural products synthesis.
Cobalt complexes are known to fixate oxygen, this characteristic enables us to carry out reactions under aerobic conditions with catalytic amount of metal complex. Designing various complexes can help us control the selectivity and efficiency of the coupling reaction in the manner of over oxidation, reaction rate and catalyst loading.
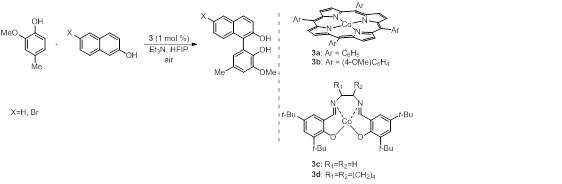
This study was initiated by cross-coupling between 2-methoxy-4-methylphenol and 6-bromo-2-naphthol using cobalt porphyrin as catalyst, under oxygen atmosphere, to obtain the desired biphenol in 57% yield. Further optimization revealed that changing the nucleophile to 2-naphthol and the catalyst to cobalt salen, increased the yield to 87% under air.

Powered by Eventact EMS