
Reaction between Silenyl Lithium and Main Group Organometalics: Transmetallation vs. Addition
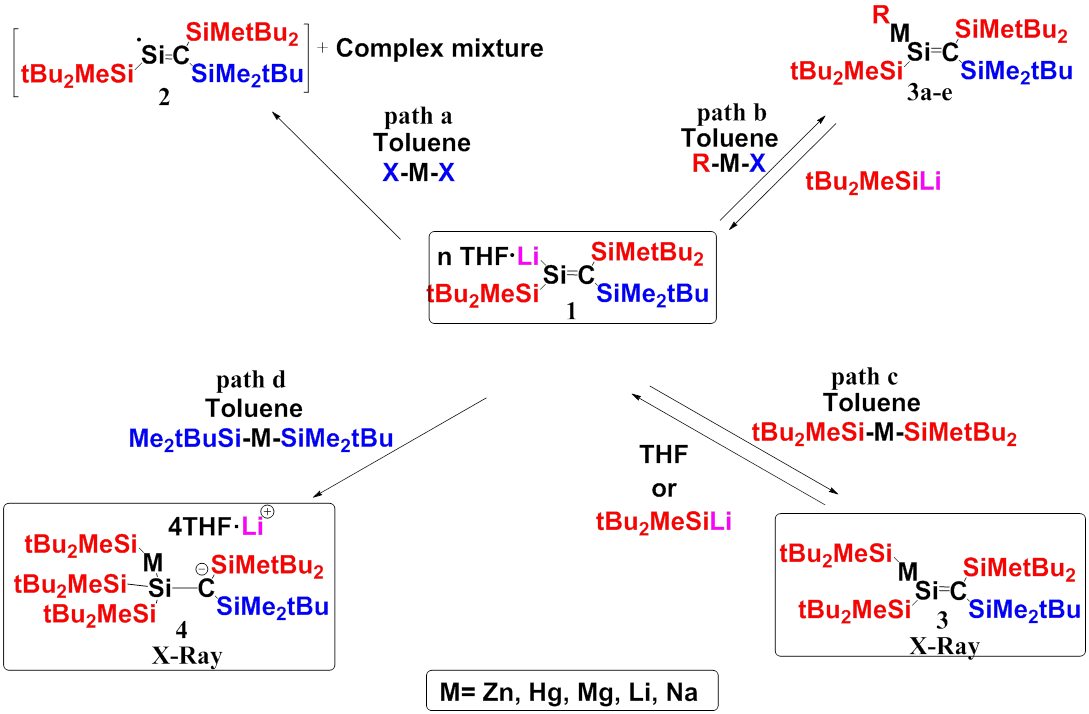
The study of the structure, properties and reactivity of doubly-bonded silicon compounds has made tremendous progress, but many challenges remain. Recently we reported the isolation of silenyl lithium 1. Now we report the synthesis of the first silenyl metals 3 and the first 1,2-dimethalomethylsilanes 4.
Reaction of 1 with MX2 (MX2=MgCl2, MgBr2 ZnCl2, HgCl2, HgF2) leads to a complex mixture of products including silenyl radical 2 and a metallic residue (Scheme, path a). Reaction of 1 with 1 equivalents of RMX (tBu2MeSiZnCl, tBuMe2SiZnCl, EtZnCl, tBuHgCl, tBu2MeSiMgBr) in toluene at 00C gave after stirring for 30 minutes the trasmetallation silenyl metal products: 3a-e, respectively (path b). Reaction of silenyl lithium 1 with 2 equivalents of (tBu2MeSi)2M (M=Zn) in toluene at 00C gave after stirring for 30 minutes 3 (path c). In contrast, reaction of 1 with 2 eq of (tBuMe2Si)2M (M=Zn, Hg, Li, Mg, Na) in toluene yields 4: the first solvent-separated ion pair of a 1,2-dimethalomethylsilanes (path d). We are currently studying the reactions of the novel 3 and 4.

Powered by Eventact EMS