DRIVING THE ACTIVATION OF HYDROGEN PEROXIDEBY TAILORED TRANSITION METALS SUBSTITUTED POLYOXOMETALATES
2School of Engineering and Science, Jacobs University Bremen, Bremen
Polyoxometalates (POMs) are molecular metal-oxo clusters, characterized by a large structural/compositional variety. The appeal of POMs in the field of oxidation catalysis mainly stems from their structural and coordination properties,since their frameworks can be considered robust, inorganic, polydentate ligands for several transition metals.
In this communication, the following transition metal substituted POMs will be proposed as oxidation catalysts with aqueous hydrogen peroxide:
(i) The Zr(IV) and Hf(IV) peroxo-heteropolytungstates [M2(O2)2(XW11O39)2]12-(M = Zr4+, X = Si (1), Ge (2); M = Hf4+, X = Si (3)),1 are able to transfer one oxygen atom to L-methionine in a aqueous environment at room temperature. The stoichiometric reaction proceeds in 1 minute, to give DL-methionine sulfoxide, whereas the corresponding sulfone can be obtained in 1-4 hours (Figure 1a). The complexes, under turnover regime, restore the reactive peroxo Hf/Zr site.1-3 can thus be considered structural model of the active sites of heterogeneous metal oxide-based systems.
(ii) Al(III) Krebs-type polyoxoanions [Al4(H2O)10(b-XW9O33)2] X=As (4) and Sb (5), have been used as tetrabutyl ammonium salts to oxidize olefins, alcohols and sulfides, in 1-2 h at 70°C, in acetonitrile (Figure 1b). When using enols as substrates, they show a remarkable chemoselectivity towards alcohol oxidation.The coordination capabilities of such POMs have been highlighted by using chiral diols, which transfer their chirality to the inorganic domain.
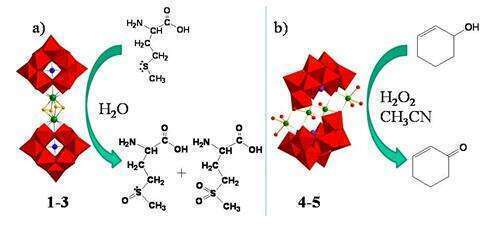
Figure 1. a) oxidation of L-methionine by Zr(IV)/ Hf(IV) substituted POMs; b) oxidation of cyclohexenol by Al(III) substituted POMs.
References
1- a) S. S. Mal, N. Nsouli, M. Carraro, A. Sartorel, G. Scorrano, H. Oelrich, L. Walder, M. Bonchio, U. KortzInorg. Chem. 2010,49, 7-9; b) M. Carraro, N. Nsouli, H. Oelrich, A. Sartorel, A. Sorarù, S. S. Mal, G. Scorrano, L. Walder, U. Kortz, M. Bonchio Chem. Eur. J.2011,17, 8371 – 8378
Powered by Eventact EMS