OXIDATION CATALYSIS IN RAW COTTON BLEACHING: THE QUEST FOR A SUITABLE MODEL
2Catexel BV, BioPartner Center Leiden, 2333 AL, Leiden
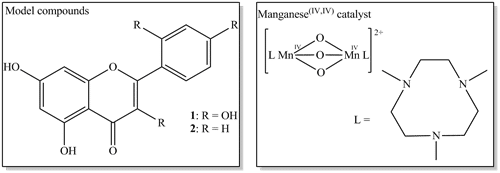
The photochemical and oxidative behaviour of morin deviates from the behaviour of raw cotton, thus it may not, in fact, be the most suitable model for raw cotton bleaching. Another flavonoid compound will be presented for use as a more relevant model. Oxidation of this new model compound will be presented with particular emphasis on the influence of factors such as pH and buffers and the effect of additives, such as sequestrants.
[i] K. Weighardt, U. Bossek, B. Nuber, J. Weiss, J. Bonvoisin, M. Corbella, S.E. Vitols, J.-J. Girerd,J. Am. Chem. Soc.,1988, 110, 7398.
[ii] (a) R. Hage, A. Lienke,Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2006, 45, 206. (b) R. Hage, A. Lienke,J. Mol. Cat. A: Chem.,2006, 251, 150.
[iii] (a) T. Wieprecht, J. Xia, U. Heinz, J. Dannacher, G. Schlingloff,J. Mol. Cat. A: Chem.,2003, 203, 113. (b) T. Topalovic, V.A. Nierstrasz, M.M.C.G. Warmoeskerken,Fibers and Polymers,2010, 11, 72. (c) E. Ember, H.A. Gazzaz, S. Rothbart, R. Puchta, R. van Eldik,Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2010, 95, 179.
Powered by Eventact EMS