
Randomized Control Trial to Compare Kangaroo Mother Care with Oral Sucrose for Pain Management in Premature Neonates on heel prick.
2Central Research Services, Charutar Arogya Mandal
3Department of Physiology, Pramukhswami Medical College
Background
Multiple studies have shown the benefits of Kangaroo mother care (KMC) and oral Sucrose on neonatal pain reduction. There is lack of head to head randomized control trials comparing the pain reduction between these two methods. Objectives To compare efficacy of Kangaroo Mother Carewith oral sucrose for pain management on heel prick with parallel group randomized control trial.
Methods
Preterm neonates (28-36 weeks gestational age) were recruited. Study interventions were done on neonates requiring heel prick as per medical management. Fifty participants per study arm were randomized to (1) Kangaroo Mother Care (KMC) group and (2) Sucrose groupwith the use of WINPEPI software. KMC was provided for 10 min in advance to procedure and continued till at least 5 min post procedure. Infants less than 32 weeks corrected age received 0.5ml of sucrose and those between 32 to 36 weeks received 1 ml sucrose 2 minutes prior to the procedure. Blinded assessment of pain was done using Premature Infant Pain Profile score on recorded videos. Trial was registered on CRTI with CTRI/2017/02/007824.
Results
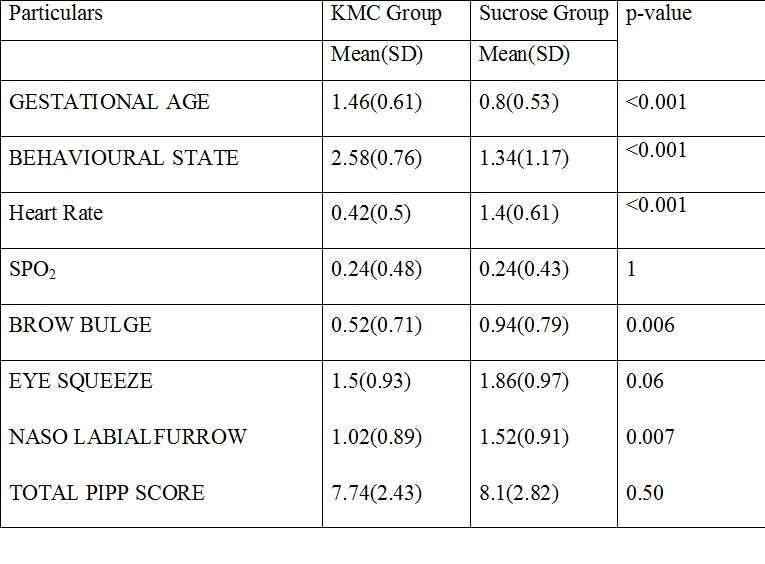
Analysis of 100 (50 KMC and 50 Sucrose group) cases were done.The mean(SD) gestational age [32.79(2.34)] weeks, age of neonate [14.04(11.10)] days and birth weight [1.62(0.35)] Kg. was similar across groups. The difference across components of PIPP is seen in Figure 1.
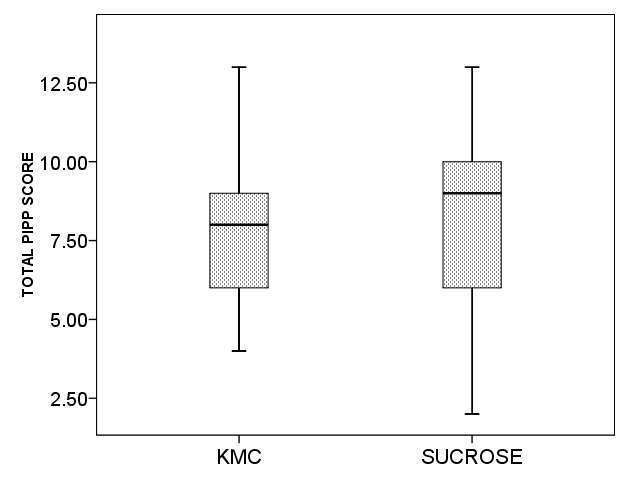
Mean(SD) PIPP score was smaller in KMC group as compared to Sucrose group but could not achieve statistical significance [7.74(2.43) vs. 8.1(2.82), p=0.50). [Figure 2].
Conclusion
There is no difference in between the pain reducing possibilities of sucrose and KMC and hence they can used alternatively as the situation demands. KMC should be preferred if possible due to other beneficial effects but sucrose is a good substitute when KMC is not feasible.
Powered by Eventact EMS