
Etoricoxib and Spinal Anesthesia as a Protective Multimodal Analgesia in Inguinal Hernia Repair: A Randomized Controlled Trial
2Faculty of Medicine, Technion - Israel Institute of Technology
Background: Inguinal hernia repair can be performed under spinal anesthesia. Optimal protective analgesic regimen, remains to be established.
Objective: Investigating preoperative etoricoxib effects within protective multimodal analgesic regimen with respect to pain control following open inguinal hernia repair.
Methods: After the approval of the Institute Ethics Committee, 60 adult patients undergoing open inguinal hernia repair participated in a randomized controlled trial. Intervention group (n=30) received 120mg etoricoxib orally 1 hour preoperatively, and 10-12mg bupivacaine with 25mcg fentanyl as spinal anesthesia. Control group (n=30) received oral placebo 1 hour preoperatively, and spinal anesthesia as above. Postoperative Visual Analog Scale pain scores at rest and on active straight leg raise, percentage of patients who received postoperative analgesia and time to first analgesic administration were recorded.
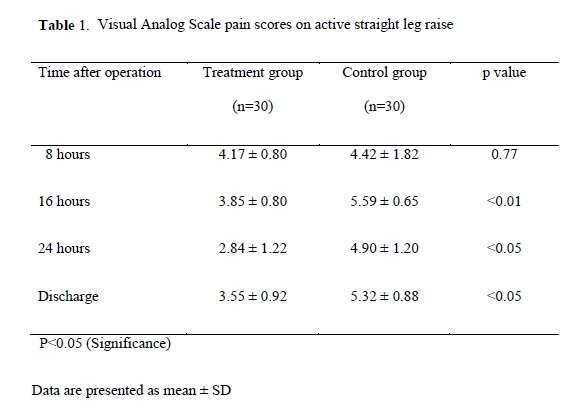
Results: Resting pain scores were significantly lower in the intervention vs. control group at 16 hours, 24 hours, and on discharge (3.00 vs. 4.35; 1.57 vs. 4.00; 1.24 vs. 3.76; p<0.05). Pain scores on active straight leg raise were significantly lower in the intervention vs. control group at 16, 24 hours, and on discharge (3.85 vs. 5.59, p<0.01; 2.84 vs. 4.90, p<0.05; 3.55 vs. 5.32, p<0.05). Percent of patients received rescue analgesia and time to first analgesic dose were significantly lower in the etoricoxib vs. the control group, (p=0. 017, p=0.001, respectively).
Conclusions: Addition of etoricoxib to spinal anesthesia as a multimodal protective regimen can improve pain control after inguinal hernia repair. The optimal dose, and generalizability to other surgical settings remain to be established.
NIHID: NCT02884986
Powered by Eventact EMS