
Cardiac Surgery Operative Risk Assessment in Patients with Imapired Systolic Left Ventricular Function Using Cardial Biomarkers
2Surgery department, Faculty of medicine, University of Novi Sad
Introduction: Recent interest has focused on cardiac biomarkers in terms of evaluating their predictive power and improving accuracy of already established risk prediction models in cardiac surgery.
Objective: To create prediction model for coronary surgery patients with impaired systolic left ventricular function on the basis of preoperative levels of certain biomarkers.
Methods: This prospective observational cohort study included 704 patients submitted to cardiac surgery with left ventricular ejection fraction less than or equal to 50%. Following biochemical analyses were performed 24 hours prior to surgery: troponin I, creatine kinase, creatine kinase MB isoenzyme, mass creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, C-reactive protein, NT-proBNP and uric acid. Postoperative mortality, postoperative onset of myocardial infarction and occurence of cerebrovascular accident and their correlation with preoperative values of listed biomarkers were registered.
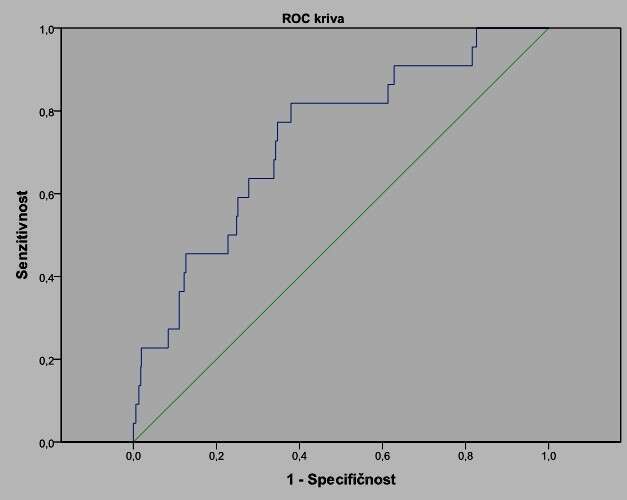
Results: The results showed that the postoperative mortality was 3.13% (22 patients) and new onset of postoperative myocardial infarction was detected in 7.95% (56) of the patients. Mean Troponin I value was significantly lower in patients with no 30-day mortality (0.044±0.345 vs. 0.371±1.262, p<0.001). NT-proBNP was significanlty higher in patients who died (3989 vs. 1701, p=0.002). A newly developed model (comprised of two factors: age and NT-proBNP value) yielded the value of C index of 0.732 which was significantly higher than the C index value of EuroSCORE II 0.664 (p<0.0005).
Conclusion: A model comprised of only two parameters (age and the value of NT-proBNP) performed better in 30-day mortality risk prediction than EuroSCORE II in patients submitted to coronary surgery.

Powered by Eventact EMS