
Green Tea Extract Improved Lipids but did not Modify Arterial Stiffness in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with premature atherosclerosis and arterial stiffening. Green tea consumption has shown beneficial effects in cardiovascular health; due to green tea polyphenols (catechins). Currently there is no clinical evidence of the effect of a green tea extract (GTE) administration on arterial stiffness in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Design and Methods: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, with no insulin treatment was conducted. Patients were randomized to 400 mg of green tea extract daily for 12 weeks or placebo. Arterial stiffness, blood pressure (BP), corporal composition, and metabolic parameters were measured at baseline and 12 weeks.
Results: At 12 weeks, statistically significant changes were found in total cholesterol, triglycerides and AIx75 between the two groups (table 1); however, no difference in aPWV, AIx, BP, fasting glucose, LDL-C, HDL-C, and anthropometric measures were observed between groups, no adverse effects were reported by patients in either group.
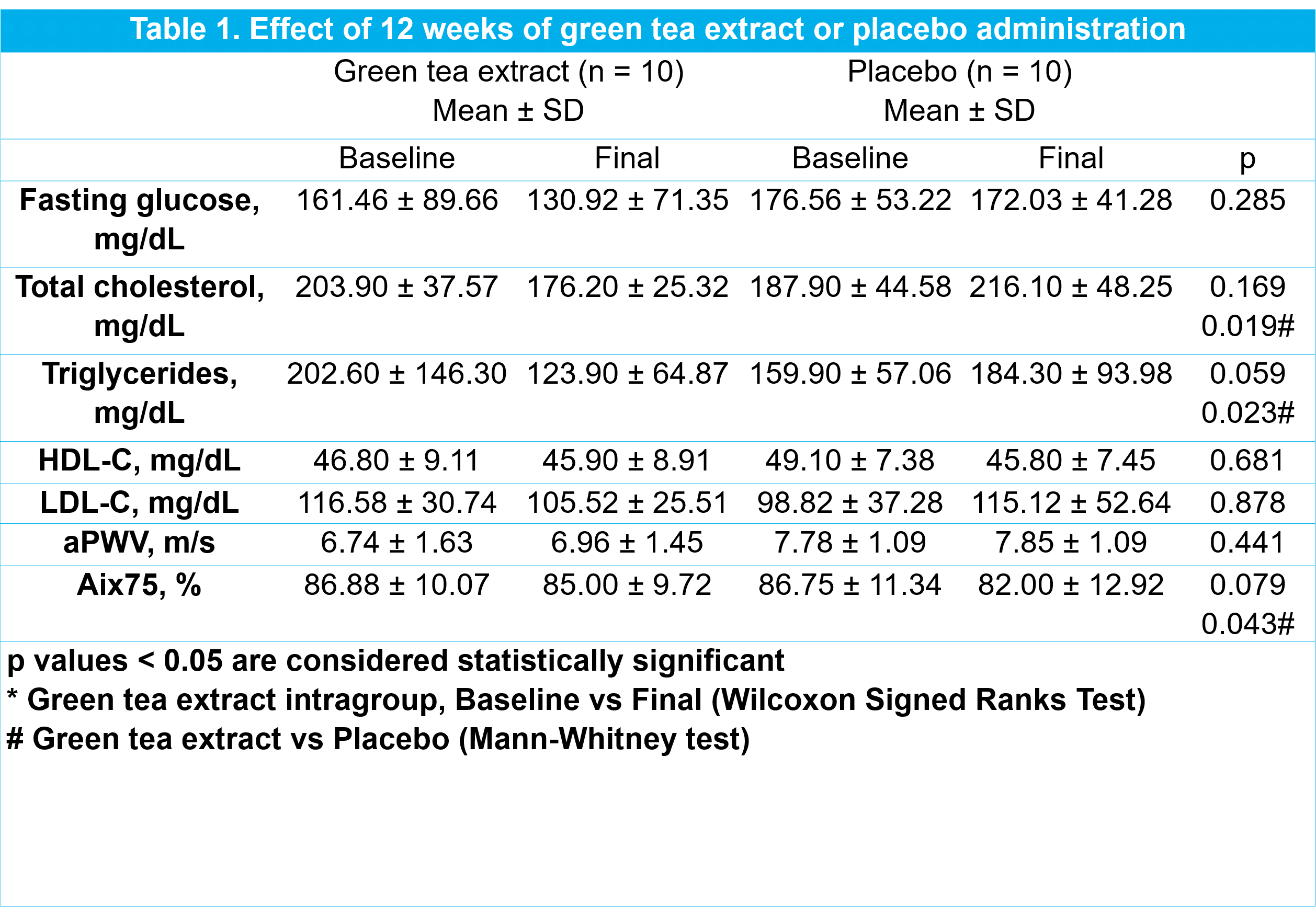
Conclusion: Administration of 400 mg per day PO of GTE for 12 weeks in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients without hypertension did not decrease aPWV, but caused a significant decrease in total cholesterol, triglycerides and AIx75 between groups.
This study shows that green tea extract may improve lipid profile in normotensive patients with type 2 diabetes.

Powered by Eventact EMS