
Quasi-Block Copolymers
Quasi-block copolymers are block copolymers consisting of conventional and supramolecular blocks, where the conventional block is end-terminated by a functionality that interacts with the supramolecular monomer (a “chain stopper” functionality).[1,2] Such materials are designed to display block copolymer-like behavior (e.g., microphase separation, micelle formation in a selective solvent) along with environmental responsiveness imparted by the supramolecular block.
The presentation will describe the basic concept and a new design of quasi-block copolymers based on a general polymeric chain stopper, which consists of polystyrene that is end-terminated with a sulfonate group (PS-SO3Li).[3] Viscosity measurements and a detailed diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy study demonstrate that PS-SO3Li can effectively interact with two types of model supramolecular polymers, forming quasi-block copolymers in solution. Furthermore, differential scanning calorimetry data and structural characterization of thin films by scanning force microscopy suggests the existence of the quasi-block copolymers architecture also in the melt. The new design considerably simplifies the synthesis of the polymeric chain stopper, thus promoting the utilization of quasi-block copolymers as smart, nanostructured materials.
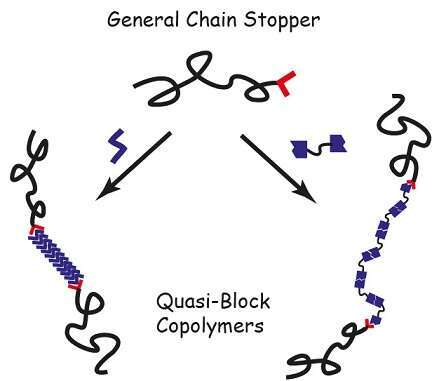
Schematic representation of the formation of different quasi-block copolymers from the same polymeric chain stopper
References
- Weiss, Esti; Daoulas, Kostas Ch.; Müller, Marcus, Shenhar, Roy. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 9773.
- Shenhar, Roy; Müller, Marcus; Daoulas, Kostas Ch.; Nealey, Paul F. “Quasi-block Copolymer Melts, Processes for Their Preparation and Uses Thereof”, U.S. patent 9,181,403.
- Sanguramath, Rajashekharayya A.; Nealey, Paul F.; Shenhar, Roy. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 10203.
Powered by Eventact EMS