
Design of Novel Aminoglycoside Derivatives with Enhanced Readthrough Activity and Low Ototoxicity
Over the past decades, certain types of aminoglycosides have demonstrated the ability to induce mammalian ribosome to readthrough disease-causing nonsense mutations, and partially restore full-length functional proteins. Despite these promising results, severe side-effects of standard aminoglycosides, among them ototoxicity - permanent hearing impairment, have limited their clinical benefit for suppression therapy. We have developed new synthetic aminoglycosides, NB-compounds, exhibiting higher readthrough capabilities to natural aminoglycosides and significantly reduced ototoxicity properties. Most recently, NB124 was shown to efficiently suppress nonsense mutations in (1) the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in CF models, (2) HEK-293 cells bearing ciliopathy–causing diseases such as Usher syndrome and (3) HDQ-P1 cancer cells containing tumor suppressor genes, such as the p53 and APC.
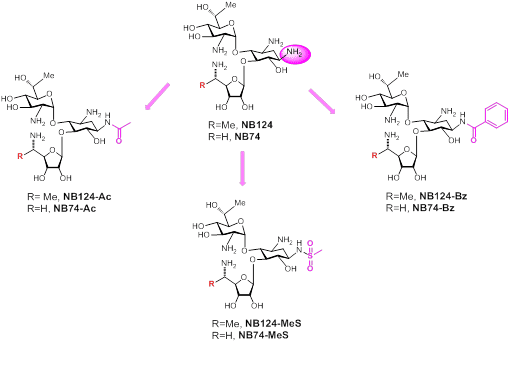
In attempts to improve therapeutic index of the lead NB-compounds, we developed a series of new modifications of the lead compounds NB74 and NB124. The synthesized compounds, NB74-MeS and NB124-MeS showed improved readthrough activity levels, with limited ototoxic response, compared with natural aminoglycosides.
Powered by Eventact EMS