
Diastolic Myocardial Mechanics in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation and Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Introduction - Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and atrial fibrillation (Afib) share common risk factors and likely coexist. Evidence of diastolic dysfunction (DDFx) required for the diagnosis of HFpEF is elusive in Afib.. Left ventricular/atrial speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE) may provide rhythm independent clues to diastolic dysfunction. We aimed to find common left ventricular/atrial myocardial mechanics parameters to demonstrate DDFx using STE in patients with Afib.
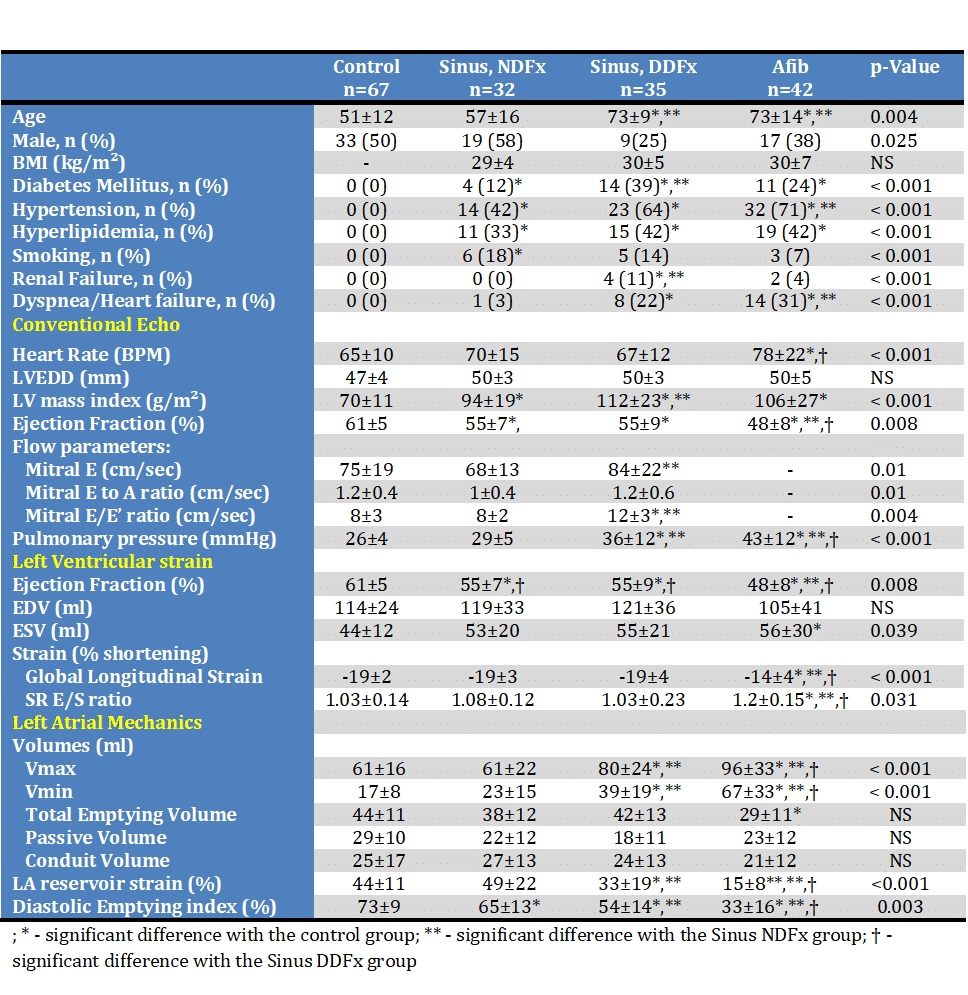
Methods – 176 echocardiographic exams of patients were studied retrospectively by STE. 109 patients with history of AFib were divided in three groups: sinus with normal diastolic function (n=32, NDFx), sinus with diastolic dysfunction (n=35, DDFx) and patient in AFib during echocardiography (n=42). These were compared to 67 normal controls. Demographic, clinical, echocardiographic and myocardial mechanics characteristics were obtained.
Results – Patients with sinus rhythm with DDFx and Afib were similar in age, were mostly women and had cardiovascular risk factors (table). Dyspnea was more prevalent compared to either controls or patients with NDFx. LV ejection fraction and global longitudinal strain were lower in the Afib group (p<0.001). LA volumes were larger and left atrial emptying and strain was lower than normal. In multivariable analysis in patient in sinus rhythm left atrial minimal volume (Vmin) was found to be the single significant correlate of DDFx (AUC 83%), and in all study patients Vmin correlated with dyspnea (AUC 80%) and pulmonary hypertension (AUC 90%).
Conclusions – Vmin may be used to identify DDFx and assist in the diagnosis of HFpEF in patients with Afib.
Powered by Eventact EMS