
Applicability of the CHADS2-VASc Score to Heart Failure Patients with Fibrillation Preserved Versus Reduced Ejection Fraction
Objective – To evaluate whether CHADS2-VASc score can similarly assess the annual risk of stroke in both HF patients with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and in HF patients with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
Methods – We investigated 3,797 patients with known AF who were hospitalized at the Sheba Medical Center under the diagnosis of acute decompensated HF. Anti-coagulation treatment was prescribed based on the patients CHADS2-VASc score or on their physician’s discretion. Subjects were divided into two groups based on their echocardiography findings: HFpEF (N=3,055) and HFrEF (N=742). The primary end point was ischemic stroke event.
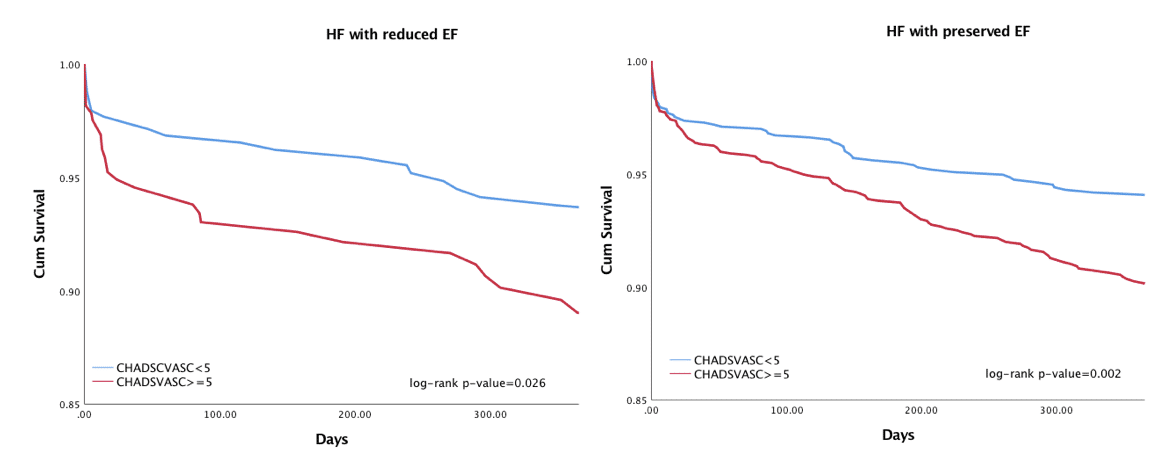
Results – Mean age of the study population was 79±11 years of whom 49% were men. Median CHADS2-VASc score for the entire study population was 5±1.6. Kaplan Meier’s survival analysis showed that at 5-years of follow-up the risk of stroke was significantly higher among patients with a high (≥5) vs. low (<5) CHADS2-VASc score in both the HFrEF and the HFpEF groups (log-rank P-value for both <0.001 [Figure]). Consistently, multivariate Cox regression proportional hazards regression analysis revealed that in both HFrEF and HFpEF patients, each point increment in CHADS2-VASc was associated with a corresponding 25% increase in the risk of stroke during follow-up (p<0.001 for both).
Conclusions – Our findings demonstrate that the CHADS2-VASc score is a powerful predictor of subsequent stroke in AF patients hospitalized with acute heart failure. The prognostic yield of the CHADS2-VASc score is similar in patients with HFrEF and HFpEF.

Powered by Eventact EMS