
Discharge Characteristics of Triangular Labyrinth Side Weirs (with Inclined Bed) Located on a Straight Channel
2Department of Water Resources Engineering, Ph.D. Candidate, Tehran University
3Department of Civil Engineering, Former Graduate Student, Sharif University of Technology
4Department of Civil Engineering, Undergraduate Student, Shiraz University
Controlling the flux of water and wastewater outlet is one of the fundamental principles of the green technology and environmental consideration. Side weir is one of the most common structures to regulate sewer overflow. In order to decrease the length of channel opening with the desired water height, the application of labyrinth side weir has been investigated. The present study is focused on the investigating the advantages of labyrinth side weirs with inclined bed (Fig. 1). Overall, more than 160 experimental laboratory tests with different hydraulic and geometry variables were conducted.
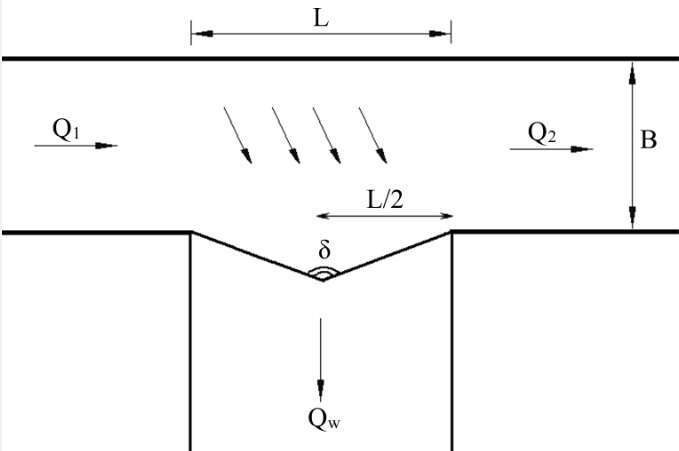
Figure 1. Plan view of triangular labyrinth side weir
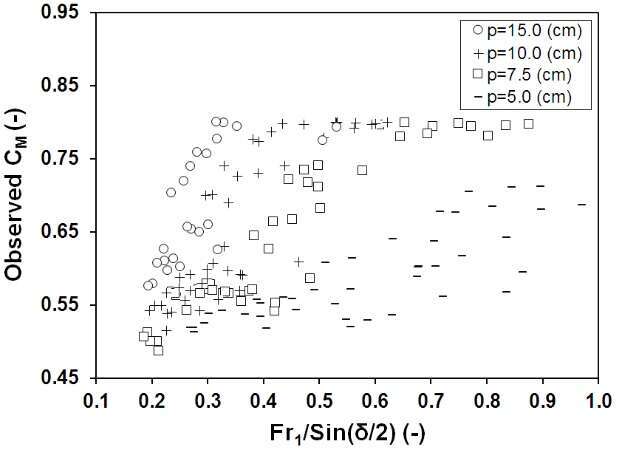
After an extensive dimensional analysis, the most precise equation generated by SPSS software for the discharged coefficient in subcritical flow in a rectangular channel is presented (Eq. 1) which is a function of four different dimensionless parameters l/B, l/L, p/h1, and Fr1/sin(d/2). Figs. 3(a–d) show the variation of discharge coefficient (CM) of triangular side weirs with an inclined plate (bed) versus these four prevailing dimensionless parameters respectively. Finally, the error analysis for measured values showed an accurate correlation with the results within ±7% (Fig. 2).

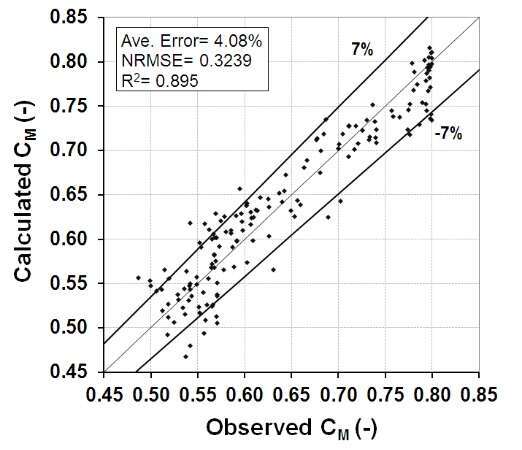
Figure 2. Observed values versus calculated values from equation 1
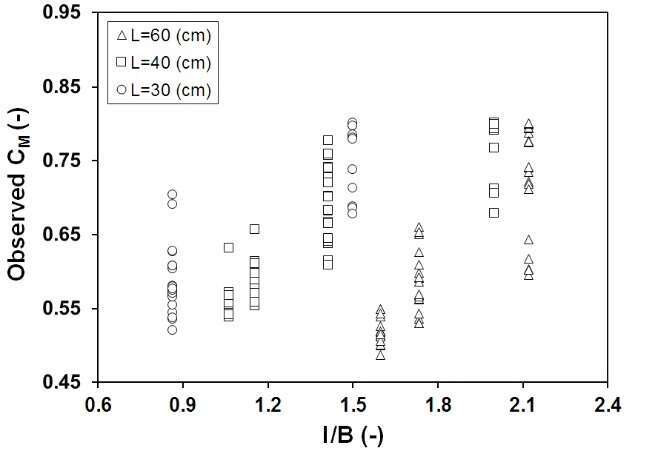
(a)
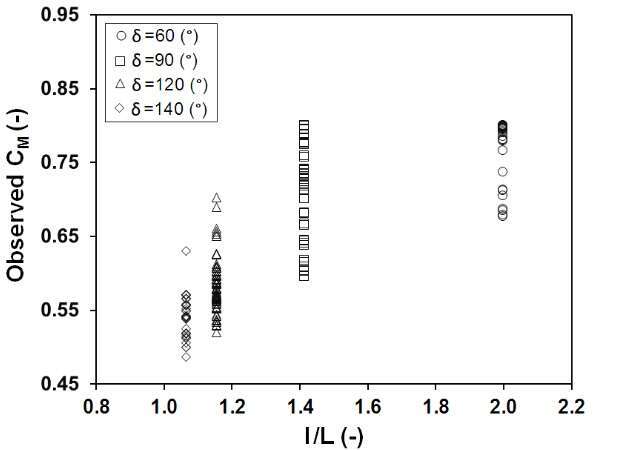
(b)

(c)
(d)
Figure 3. Measured discharge coefficient versus dimensionless parameters; (a) l/B, (b) l/L, (c) p/h1, (d) Fr1/sin(d/2)
The main contributions can be summarized as follows:
- Like other types of labyrinth weirs, triangular side weirs (with inclined plate) can also significantly increase the lateral discharged water, compared to the normal side weir with the same geometry and flow conditions. They could also be applied as an effective solution for increasing the storage capacity.
- Application of triangular side weirs (with inclined plate) helps control any fluctuated flow near the downstream end of the side weir which is a significant advantage when the flux deals with sediments or waste materials.
- The vertex angle of the inclined labyrinth side weir can act as a control parameter. It means that when "d" is between 60-140 degrees, the lower value for "d" presents the higher value for CM.
- Finally, nonlinear relation Eq. 1 was introduced for prediction of the discharge coefficient CM of triangular side weirs with one cycle and inclined bed.
Powered by Eventact EMS