
The Effect of Tyrosine and Phenylalanine Based Carbon Dots on IAPP Aggregation
Many human diseases are associated with misfolding, and fibril formation of proteins. For example, amyloid-β in Alzheimer’s and IAPP in type 2 diabetes are caused by the formation of an insoluble, rich β sheet fibrils of the different proteins. 1
Polyphenols are a group of natural or synthetic molecules containing aromatic phenolic rings.1,2studies have showed that polyphenols can interact with amyloid fibrils, interfere with the fibril formation.2, It is suggested that the interaction mechanism between the amyloid fibrils and the polyphenols is through aromatic interactions between the phenols and the aromatic residues in the protein.2
Carbon quantum dots (C dots) are carbon based Nano partials with a graphite-based core and an outer layer having functional groups originated from their building blocks reactants. The C dots are of a great interest due to their size (<10nm), their fluorescence emission, biocompatibility and low toxicity.3Recently it was discovered by Jelinek`s lab that L-Lys based C dots can interfere with the aggregation of Prion.3
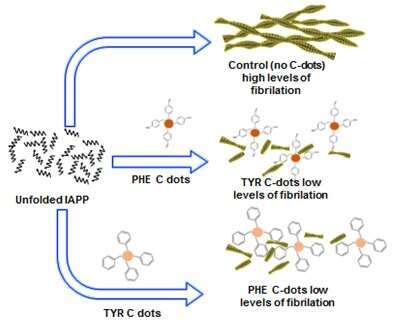
The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of Tyrosine and Phenylalanine C dots have on IAPP aggregation. The research will focus on the kinetics and morphology aspects of the fibrils formation under the presence and absence of the C dots.
- Ngoungoure, V. L. N., Schluesener, J. & Paul, F. Natural polyphenols binding to amyloid : A broad class of compounds to treat different human amyloid diseases. Mol. Nutr. food Res. 8–20 (2015). doi:10.1002/mnfr.201400290
- Porat, Y., Abramowitz, A. & Gazit, E. Inhibition of amyloid fibril formation by polyphenols: Structural similarity and aromatic interactions as a common inhibition mechanism. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 67, 27–37 (2006).
- Arad, E. & Bhunia, S. K. Lysine-Derived Carbon Dots for Chiral Inhibition of Prion Peptide Fibril Assembly. Adv. Ther. 1800006, 1–8 DOI:10.1002/adtp.201800006 (2018).
Powered by Eventact EMS