
Contributed
Bimanes reconsidered: From fluorescent dyes to ligands
2Department of Chemical Research Support, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
3Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology, Ariel University, Ariel, Israel
Bimanes are heterocyclic compounds, the molecular structure of which is based on the 1,5-diazabicyclo[3.3.0]octadienedione framework (Scheme 1). These compounds, which were introduced four decades ago by Kosower and coworkers,[1] exist in two diastereomeric forms, i.e., syn and anti. The syn-bimanes are strongly fluorescent, and are primarily used as fluorescent dyes for biological labeling, whereas the anti-bimanes fluoresce only weakly. All bimanes bear the typical hallmarks of a metal-binding ligand, i.e., both O- and N-donors, as well as a sterically-accessible π system. However, despite being known and used for forty years, mostly in biological media that inevitably contain metal ions, the coordination chemistry of bimanes, and its spectroscopic implications, has not been studied.
We recently reported the first examples of metal-coordinated bimanes, in the form of cationic Pd(II) and Na(I) complexes containing syn-(Me,Me)bimane as an O-donor ligand (Scheme 1).[2],[3] Our investigation has since been expanded to include complexes of this representative bimane with other metal ions, e.g., Li(I), K(I), Mg(II), Ca(II) and Zn(II). In addition, we have introduced a new family of bimanes - thioxobimanes - by sequentially substituting sulfur for the carbonyl oxygen atoms of syn-(Me,Me)bimane, and have begun exploring their coordination chemistry by preparing a series of coinage-metal complexes. Our recent findings pertaining to the coordination chemistry of syn-(Me,Me)bimane will be presented, along with the chemistry of its new thioxo variants. In addition, we shall address the observed effects of metal ions on bimane fluorescence, an aspect which has been overlooked in the past, and may have ramifications for the use of bimanes in metal-containing media.
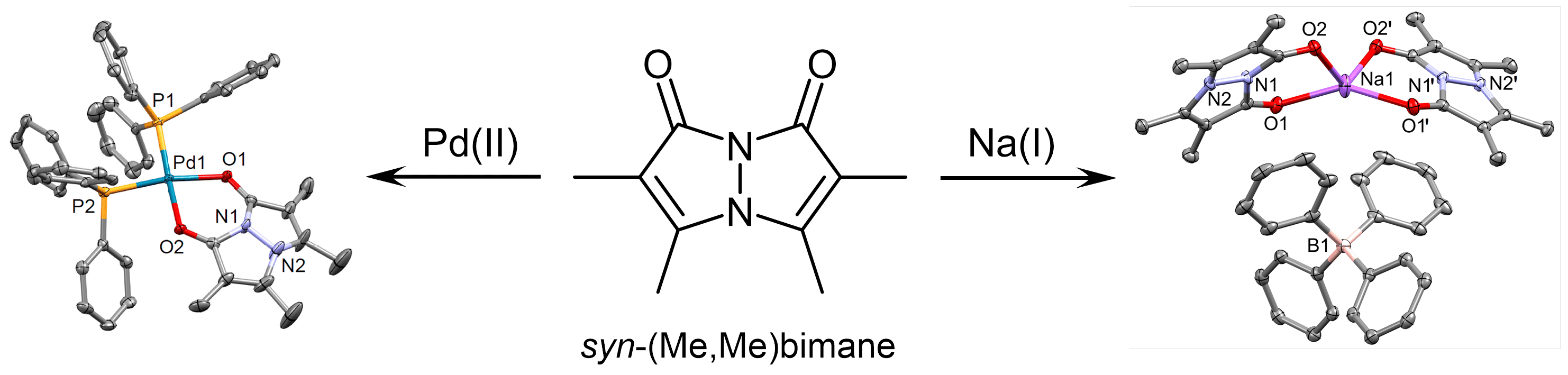
Scheme 1. Complexes of syn-(Me,Me)bimane with Pd(II) (left) and Na(I) (right).
[1] Kosower, E. M.; Pazhenchevsky, B.; Hershkowitz, E., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1978, 100, 6516-6518.
[2] Das, P. J.; Diskin-Posner, Y.; Firer, M.; Montag, M.; Grynszpan, F., Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 17123-17131.
[3] Roy, A.; Das, P. J.; Diskin-Posner, Y.; Firer, M.; Grynszpan, F.; Montag, M., New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 15541-15545.
Powered by Eventact EMS