
A Brillouin Fiber Laser at 2-µm Based on a Step-index Tellurite (TeO2) Optical Fiber
2Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire Carnot de Bourgogne, Université Bourgogne Franche-Comté
Abstract: We experimentally demonstrate a single frequency Brillouin fiber laser at 2-µm using a passive fiber ring cavity. A low lasing threshold of 70 mW was achieved with a 2m-length step-index tellurite-glass optical fiber.
Stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in optical fibers is a nonlinear process with important applications such as distributed optical fiber sensing, microwave photonics, optical storage, and fiber lasers [1,2]. The latter application has attracted significant interest as highly coherent laser sources with sub-Hz linewidth can be achieved using SBS in optical cavities. To date, most of Brillouin fibers lasers (BFLs) have been designed at 1.55 µm. However, for a range of mid-IR applications like high resolution molecular sensing and coherent LIDAR, there is a need to develop laser sources at longer wavelength range [3,4].
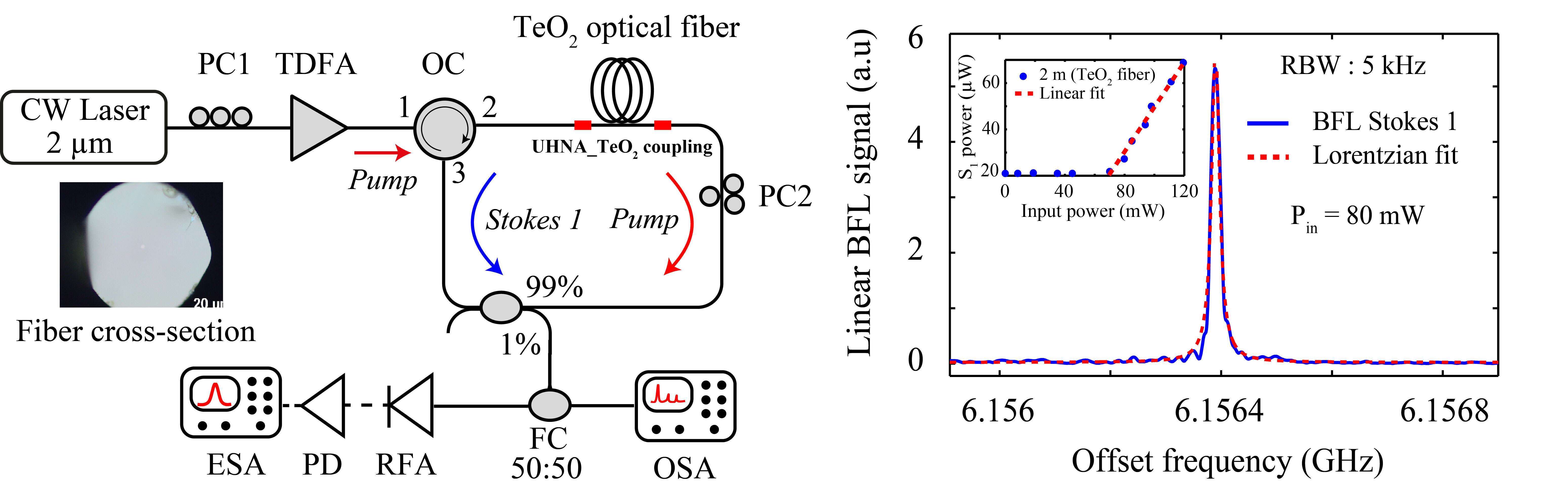
Fig. 1. Left: Experimental setup for Brillouin fiber laser. CW: Continuous wave, TDFA: Thulium doped fiber amplifier, OC: Optical circulator, PC: Polarization controller, UHNA: Ultra-High Numerical aperture coupling fiber, ESA: Electrical spectrum analyzer, PD: Photodiode, RFA: Radiofrequency amplifier, FC: Fiber coupler, OSA: Optical spectrum analyzer. Right: Output laser RF spectrum, and inset: Stokes Brillouin power diagram. RBW: Resolution bandwidth
In this work, we demonstrate Brillouin lasing around 2-µm using a step-index tellurite-glass optical fiber as the Brillouin gain medium. The experimental setup and fiber cross-section are shown in Fig. 1 (left), while Fig.1 (right) shows the output laser RF spectrum and the Stokes power diagram. The SBS (Stokes 1) cavity pumped at 2-µm exhibits a lasing threshold of only 70 mW and a high Brillouin gain efficiency estimated to be 10.5 m-1 W-1. The Brillouin frequency shift was 6.156 GHz. Finally, the beat signal linewidth between the Brillouin Stokes and the pump wave was measured to be 48 kHz. We are working on lowering the linear losses within the cavity to increase the lasing efficiency.
References
- A. Kobyakov, M. Sauer, and D. Chowdhury, "Stimulated Brillouin scattering in optical fibers," Adv. Opt. Photonics 2(1), 1–59 (2010).
- C. A. Galindez-Jamioy and J. M. Lopez-Higuera, "Brillouin distributed fiber sensors: an overview and applications," J. Sens. 204121, (2012).
- Y. Luo, Y. Tang, J. Yang, Y. Wang, S. Wang, K. Tao, L. Zhan, and J. Xu, "High signal-to-noise ratio, single-frequency 2 μm Brillouin fiber laser," Opt. Lett. 39(9), 2626–2628 (2014).
- K. Hu, I. V. Kabakova, T. F. S. Büttner, S. Lefrancois, D. D. Hudson, S. He, and B. J. Eggleton, "Low-threshold Brillouin laser at 2 μm based on suspended-core chalcogenide fiber," Opt. Lett. 39(16), 4651–4654 (2014).

Powered by Eventact EMS