
Light-controlled dynamic self-assembly of Au nanoparticles in aqueous and non-aqueous solutions
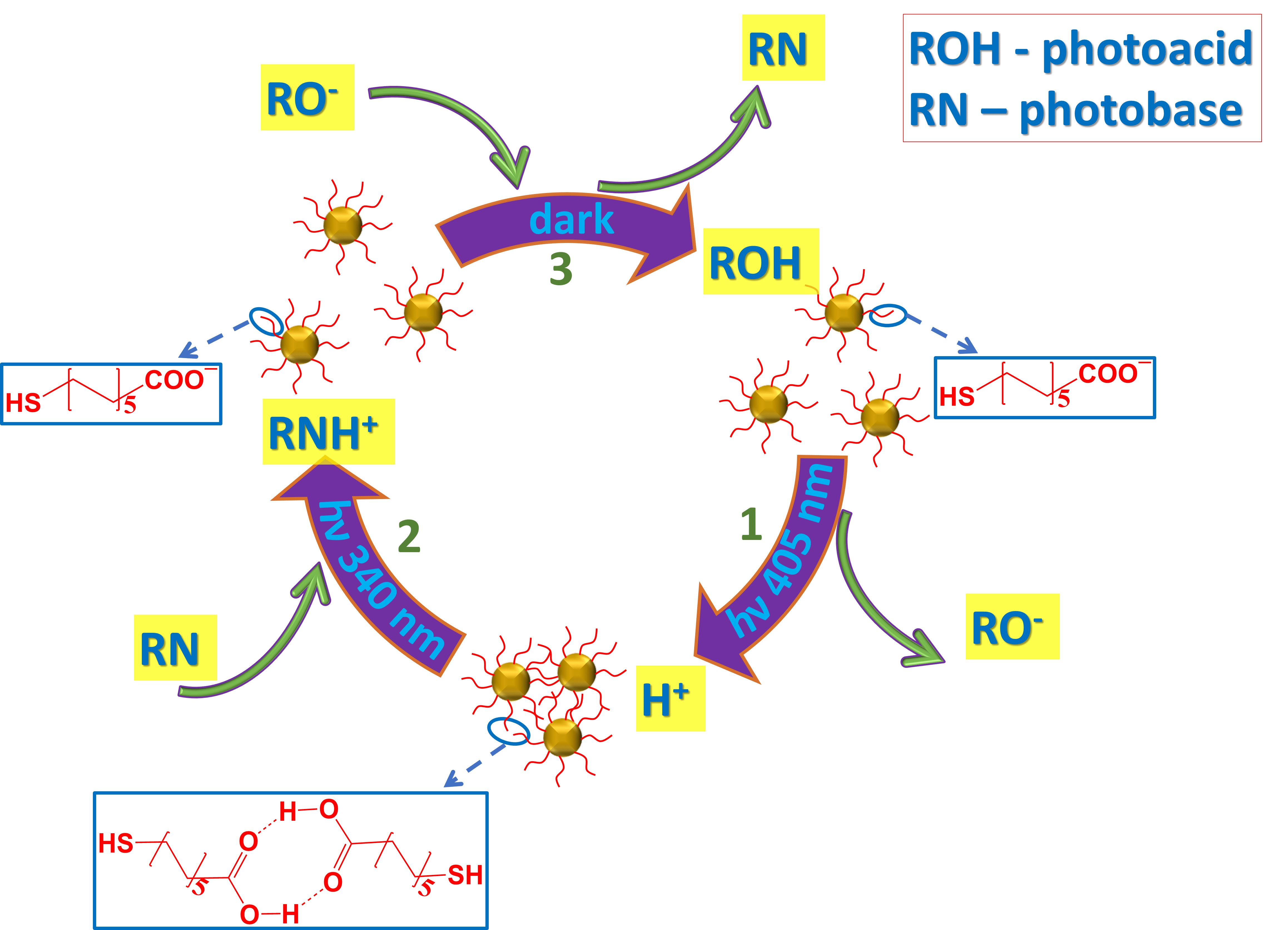
Dynamic self-assembly is a fundamental process both in biological systems (e.g., in replication, self-healing, cytoskeletal transport and more), as well as in many nanotechnological systems. Here, we present an example of artificial dynamic nano-system in the form of light controlled reversible aggregation of Au nanoparticles (AuNPs), functionalized with pH sensitive ligands. The dynamicity of the process is provided by photoacids and photobases, which are aromatic molecules that display properties of weak acid/base in their ground electronic state, but exhibit great pKa drop or increase, respectively, in their excited state. In aqueous system, we used photoacid to mediate excited state proton transfer (ESPT) effect, resulting in AuNPs protonation and subsequent aggregation. The reverse process, leading to the dispersion of nanoparticles, was mediated by a photobase, capable to capture protons in its excited state. The diversity of light responsive compounds which can be employed in functional nano-systems, can be extended by introduction of another kind of photobases, able to release hydroxide in their excited state. Thus, in addition to ESPT driven systems, we also developed dynamic AuNPs-photobase systems, where self-assembly of AuNPs was driven by excited state hydroxide transfer process.
Powered by Eventact EMS