
Contributed
Simple, straightforward, enantio- and diastereodivergent access to acyclic polyfunctionalized aldehydes by a palladium-catalyzed remote heck reaction
The access to stereocontrolled and functionalized quaternary stereocenters is challenging owing to its high steric hinderance.[1] Yet, remote functionalization proved to be an efficient strategy to overcome these synthetic issues.[2] Based on the combined use of cyclopropylmethanol,[3] and Heck reaction,[4] we anticipated that the strain release of cyclopropyl moieties would drive the Heck reaction of alcohol 1 towards the formation of the aldehyde 2 (Scheme 1).
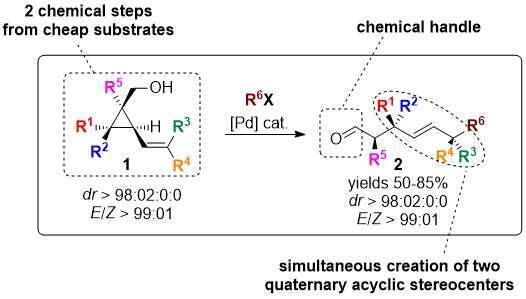
Scheme 1 Access to polyfunctionnal aldehydes through remote Heck reaction
To our delight the transformation was highly diastereoselective, providing a single (E)-diastereomer.[5] The efficiency of the approach is supported by a straightforward and modular synthesis of alkenyl cyclopropylmethanol moieties. A representative scope and mechanistic insight will be presented.
[1] I. Marek, Y. Minko, M. Pasco, T. Mejuch, N. Gilboa, H. Chechik, J.P. Das, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 2682.
[2] a) J. Bruffaerts, D. Pierrot, I. Marek, Org. Biomol. Chem.2016, 14, 10325; b) A. Vasseur, J. Bruffaerts, I. Marek, Nature Chem. 2016, 8, 209.
[3] a) A. Marsawa, D. Didier, T. Zabrodski, M. Schinkel, L. Ackermann, I. Marek, Nature 2015, 505, 199 ; b) A. Vasseur, L. Perrin, O. Eisenstein, I. Marek, Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 2770.
[4] a) E.W. Werner, T.-S. Mei, A.J. Burckle, M.S. Sigman, Science 2012, 338, 1455 ; b) T.-S. Mei, H.H. Patel, M.S. Sigman, Nature 2014, 508, 340.
[5] J. Bruffaerts, D. Pierrot, I. Marek, Nature Chem. 2018, 10, 1164.
Powered by Eventact EMS