
Cardiolipin mediates curcumin interactions with mitochondrial membranes
2Ilse Katz Institute for Nanoscale Science and Technology, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel
3Department of Clinical Biochemistry and Pharmacology, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel
4Department of Surgery, Drexel University College of Medicine, Philadelphia, PA, USA
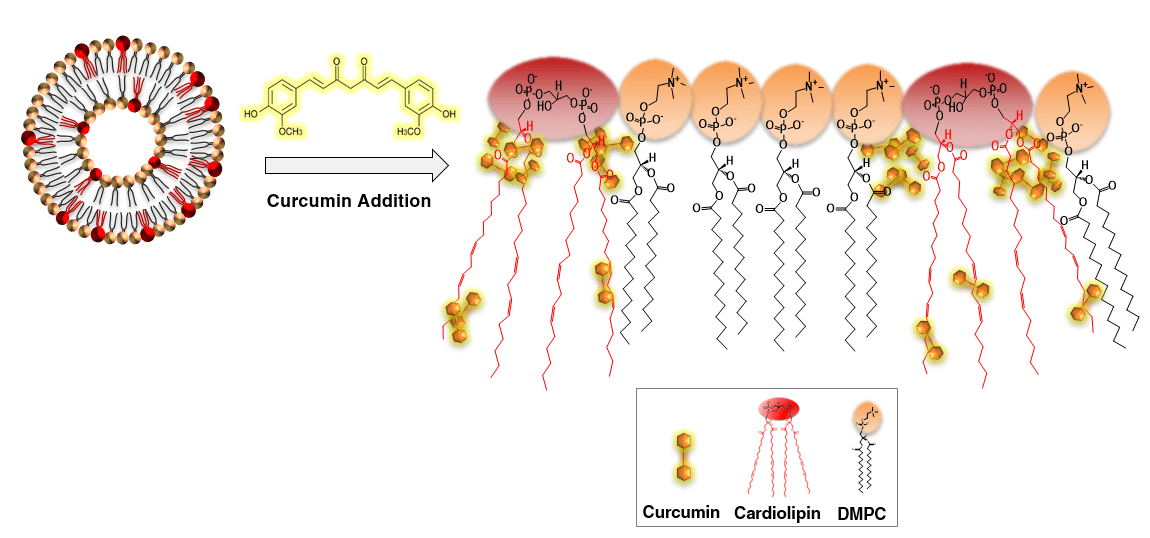
Curcumin, the main molecular ingredient of the turmeric spice, has been reported to exhibit therapeutic properties for varied diseases and pathological conditions. While curcumin appears to trigger multiple signaling pathways, the precise mechanisms accounting for its therapeutic activity have not been deciphered. Here we show that curcumin exhibits significant interactions with cardiolipin (CL), a lipid exclusively residing in the mitochondrial membrane. Specifically, we found that curcumin affected the structures and dynamics of CL- containing biomimetic and biological mitochondrial membranes. Application of several biophysical techniques reveals the CL-promoted association and internalization of curcumin into lipid bilayers. In parallel, curcumin association with CL containing bilayers increased their fluidity and reduced lipid ordering. These findings suggest that membrane modifications mediated by CL interactions may play a role in the therapeutic functions of curcumin, and that the inner mitochondrial membrane in general might constitute a potential drug target.
Powered by Eventact EMS