
The renaissance of Sabatier CO2 hydrogenation catalysis
The 100-year old Sabatier reaction, i.e. catalytic CO2 hydrogenation, is now seeing a renaissance due to its application in Power-to-Methane processes for electric grid stability and potential CO2 emission mitigation [1]. To date however, the fundamentals of this important catalytic reaction are still a matter of debate. Recently, we have showed how the mechanism of catalytic CO2 methanation depends on Ni nanoparticle size using a unique set of well-defined silica-supported Ni nanoclusters (in the range 1-7 nm) and advanced characterization methods (i.e., operando FT-IR, and operando quick X-ray absorption spectroscopy) [2]. We now show fundamental theoretical concepts proving why CO2 is structure sensitive, and how CO2 is activated mechanistically. By linking spectroscopic descriptors to these fundamental findings we ultimately leverage our understanding with a toolbox of structure sensitivity, and a library of reducible and non-reducible supports (SiO2, Al2O3, CeO2, ZrO2 and TiO2), tuning the selectivity and activity of methanation over Ni [3]. For example, we show that CO2 hydrogenation over Ni can and does form propane (Figure 1). This work contributes to our ability to produce “ideal” catalysts by improving the understanding of the catalytic sites and reaction pathways responsible for higher activity and even C-C coupling.
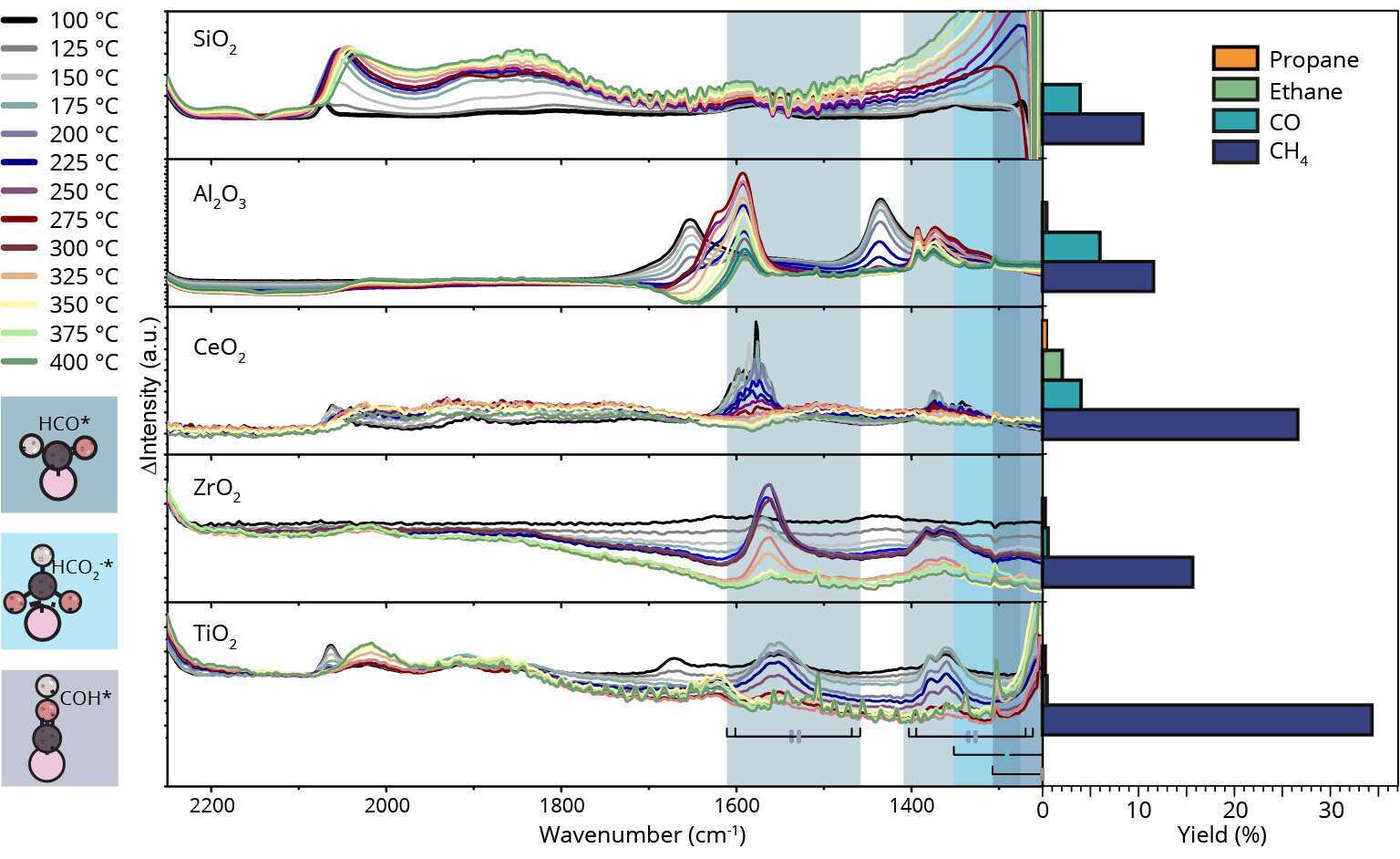
Figure 1: Operando FT-IR spectra of a series of Ni-based catalysts under CO2 hydrogenation conditions at different temperatures and the spectral regions of CO(ads) and formate species (left), and respective yield of methane, CO(g) and C-C coupling products (ethane and propane) at 300°C (right). The Ni-based catalysts are made from different support oxides.
References
[1] Vogt, C.; Monai, M.; Kramer, G. J.; Weckhuysen, B. M.; Nature Catalysis, Accepted Article.
[2] Vogt, C.; Groeneveld, E.; Kamsma, G.; Nachtegaal, M.; Lu, L.; Kiely, C.J.; Berben, P.H.; Meirer, F.; Weckhuysen, B.M.; Nature Catalysis 1, (2018) 127–134.
[3] Vogt, C.; Sterk, E. B.; Monai, M.; Palle, J.; Zijlstra, B.; Groeneveld, E.; Berben, P. H.; Boereboom, J. M.; Hensen, E. J. M.; Meirer, F.; Filot, I. A. W.; Weckhuysen, B. M; Manuscript under Review.
Powered by Eventact EMS