
Umpolung Morita-Baylis-Hilman C-H functionalization of unsaturated ketones via in situ formation of electrophilic enolonium species
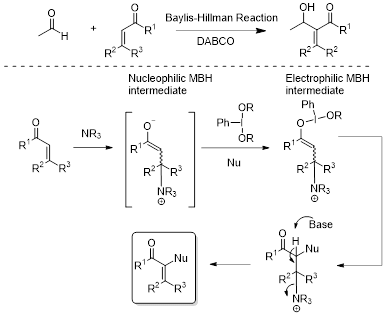
The Morita-Baylis-Hillman reaction is a unique reaction for C-H functionalization of the α-position of activated α,β unsaturated ketones.1 The classical reaction involves formation of a nucleophilic enolate through the reversible conjugate addition of an amine with subsequent reaction with an aldehyde (See Scheme). We have explored and developed a novel concept that allows the umpolung of the in situ formed enolate into an electrophilic enolonium species by the action of hypervalent iodine reagents (See Scheme for proposed mechanism).2 This new concept has been utilized in several C-O bond forming reactions including α-tosylation, -triflation, and -acetoxylation).
1) Morita, K.-i.; Suzuki, Z.; Hirose, H. Chem. Soc.Japan 1968, 41, 2815.
2) Arava, S., Kumar, J. N., Maksymenko, S., Iron, M. A., Parida, K. N., Fristrup, P., & Szpilman, A. M. Chem. 2017 129, 2643-2647.
Powered by Eventact EMS