
Developing and Implementing Asthma Severity and Control Screening in a Large Urban Health System
Background: Asthma severity or level of control classification is the first step in asthma management. To optimize asthma management, screening must be done at each visit.
Objectives: 1) To develop and implement asthma severity and control screening within electronic health record (EHR) of a large urban health system; 2) To increase asthma screening from 0% to 80% by December 2020.
Methods: We developed an asthma screening algorithm in EHR based on national guidelines. Screening is conducted by the nursing staff prior to patient being seen by the provider. Based on responses, severity/control classification is calculated and displayed in EHR. Classic Quality Improvement tools such as the Model for Improvement and Plan Do Study Act (PDSA) cycles were used to incorporate changes into daily workflow. Practice Advisory Board meets monthly to discuss barriers to implementation and identify solutions. The Board makes decisions on adopting successful strategies and brainstorm new strategies to address barriers.
Results: This project is ongoing and preliminary results are available from 3 practices: small pediatric, large pediatric and family medicine practices. To date, a total of 4,057 screenings have been completed. Screening rates improved from 0% to 78.6% in a small pediatric practice, from 0% to 66.7% in a large pediatric practice, and from 0% to 38.7% in a family practice (See figures).
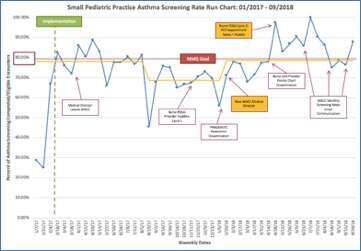
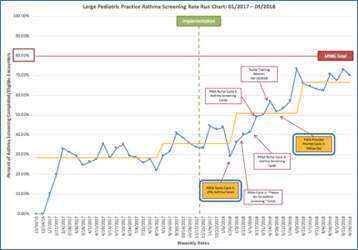
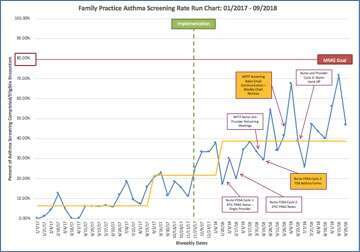
Challenges encountered include: competition with other nurse-completed screenings; screening questions are available in English; nursing staff shortages; nurses forgetting to conduct screening; and caregiver not knowing information about child’s asthma.
Conclusion: We developed an asthma screening algorithm within EHR, trained nursing staff and implemented patient screening at the time of clinic visit allowing providers take action on asthma management based on the screening result. Further collaborative efforts are needed to improve and sustain screening rates with the ultimate goal of improving patient clinical outcomes.
Powered by Eventact EMS