
Statistical Relationship of Overweight, Obesity and High Blood Pressure in Children Based on the Analysis of Russian Big Data
2Department of Development, CRС Medass, Russia
3Cardiology Research Department, Federal State Autonomous Educational Institution of Higher Education I.M. Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (Sechenov University), Russia
It is considered, overweight and obesity are a risk factor for hypertension and high blood pressure (HBP). In 2014, big data of health exam in Russian health centers are available for analysis under grant of the Russian Science Foundation.
Aim of the Work: Estimate statistical relationship of overweight, obesity, and HBP in children based on the analysis of Russian big data.
Materials and Methods: The present study used data from 107,015 children aged 6-18 who visited Russian health centers in 2009–2015. The survey results are accumulated in the Federal Information Resource of Health Centers.
The analysis included the calculation of the Spearman correlation coefficient between blood pressure (SBP, DBP) and BMI and body fat mass (%FM) for each month of life and an estimate of the prevalence of HBP (SBP or DBP > the height-age standard) for children with normal weight (NW) and overweight or obesity (Ov/Ob, by BMI).
Results and Discussion: The correlation coefficient for BMI and SBP had pronounced fluctuations in 0.15-0.40. The general age trend (polynomial approximation) has a maximum at 12.5 years (r=0.30). The general age trend of correlation of %FM and SBP has a maximum at 8 years and 4 months (r=0.25). Thus, SBP is 9% determined by changes in BMI and 6% – in %FM. The correlation values with DBP are about 0.1 less than with SBP.
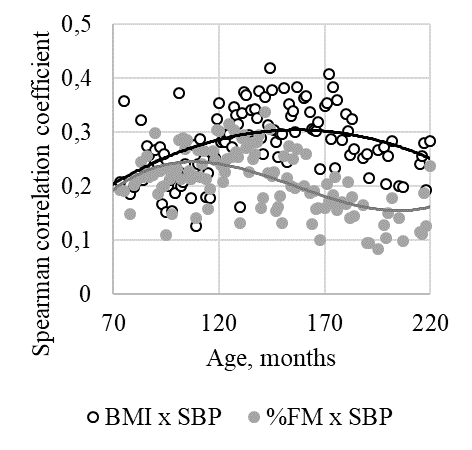
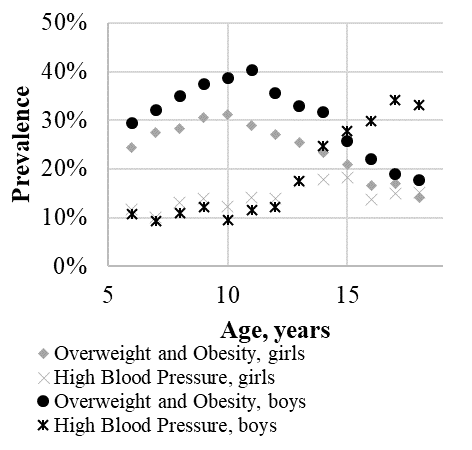
The presence of Ov/Ob increased the prevalence HBP: 16.6% for boys and 11.5% for girls with NW and 26.3% and 24.4% for boys and girls with Ov/Ob.
Conclusions: The analysis of Russian big data showed the presence of a correlation of BMI and %FM with SBP and DBP. The presence of Ov/Ob increased the prevalence of HBP by 2 times.
Acknowledgment:
This work was supported by grant No. 14-15-01085 of the Russian Science Foundation (Hwad: V. Starodubov)
Powered by Eventact EMS