
Application of Botulinum Toxin in a Tertiary Hospital in Mexico, in a Paediatric Patient Diagnosed with Achalasia Type 2, as a Therapeutic Alternative: A Case Report
Background: An oesophageal motility disorder characterized by aperistalsis and failure to relax the lower oesophageal sphincter. Patients present with dysphagia to solids and liquids, cough, regurgitation, chest pain and weight loss. There are various forms of treatment, including Heller myotomy with fundoplication, balloon dilation or local application of botulinum. To date, there is little experience in the application in paediatric patients.
Objective: Describe the application and results of botulinum toxin as an alternative treatment in Achalasia.
Method: A case report of a patient who received the application of botulinum toxin as an alternative treatment.
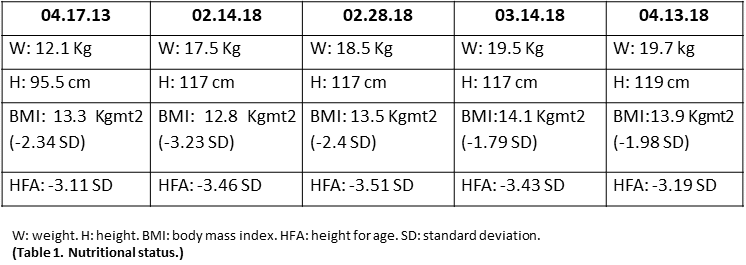
Results: Achalasia was diagnosed at 4 years of age, with endoscopy and high-resolution oesophageal manometry. A Heller`s Myotomy plus Dor-type fundoplication was performed, without improvement, then 4 sessions of oesophageal dilatation were performed without improvement. At 10 years of age, the patient does not improve in his quality of life, so it was decided to administer 80 IU of botulinum toxin in total endoscopically, 20 IU per quadrant to 1 cm of the oesophagogastric junction. 24 hours after the endoscopic application, the patient tolerates liquids and finally chopped properly, at 6 days post botulinum toxin application he tolerates 100% of the solid diet, without the presence of chest pain, regurgitation, vomiting, dysphagia or a cough. It was decided to discharge 14 days after the application. Patient has adequate improvement in nutritional status.
Conclusion: The application of botulinum toxin is a therapeutic alternative for refractory cases of patients with Achalasia. We consider that the use of botulinum toxin is safe and effective with a response rate of up to 75%. There is a little experience described in the literature in paediatric patients, so it is recommended to carry out prospective studies.
Powered by Eventact EMS