
THE INFLUENCE OF THE PROCESSING STRATEGY ON THE DYNAMIC RESPONSE OF SLM-AlSi10Mg ALLOY
2Materials Engineering, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel
One type of additive manufacturing (AM) technique, the selective laser melting (SLM), attracts great interest for many industrial applications requiring near-net shape manufacturing of lightweight components, as well as enhanced mechanical properties. The SLM-AlSi10Mg alloy is one of the most popular (lightweight) materials used in engineering structures, featuring good castability, good weldability and well-known solidification behavior. The quasi-static properties of the SLM-AlSi10Mg are comprehensively characterized. On the other hand, the dynamic behavior suffers from serious knowledge gap. Due to unpredicted impact situations in service conditions that can expose this alloy to dynamic loading, it is imperative to investigate its dynamic behavior.
The focus of this presentation is on the dynamic response of the SLM-AlSi10Mg alloy, in the "as built" state, at room temperature. Dynamic properties were experimentally characterized using the split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) apparatus under strain rates ranging from 700 to 6700 1/s. This fundamental study was set to correlate dynamic properties to some of the manufacturing process. Therefore, the experiments were carried out on samples distinguished by their manufacturing process, particularly scanning pattern, scan speed and beam energy, the alternation in the manufacturing reflects in the true stress true strain behavior (fig a). To better understand the effects of manufacturing strategy and the form of plastic compliance, this study is accompanied by systematic microstructural characterization (fig b), textural investigations (fig c) and residual stress analysis (fig d) using various Electron and X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) techniques namely, the Electron Backscattered Diffraction (EBSD), Transmission-EBSD (T-EBSD), Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and XRD techniques
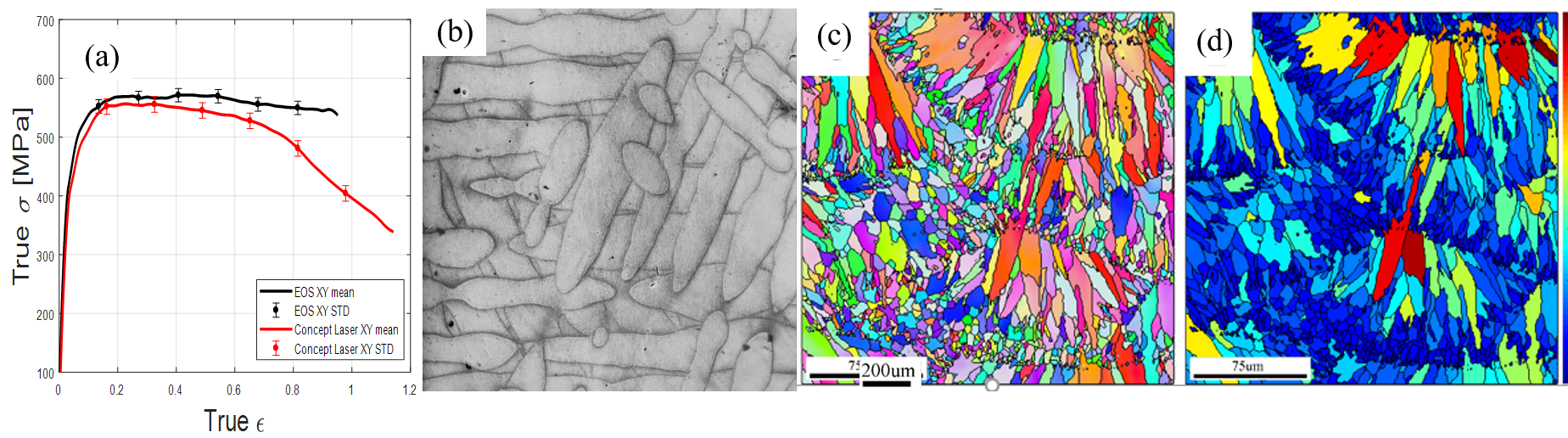
(a) SHPB results for both manufacturing techniques, (b) SLM image of SLM AlSi10Mg building surface, (c) the building surface side view inverse pole figure, (d) the building surface side view grain orientation spread
Powered by Eventact EMS