
BIOLOGICAL SILICA FORMATION IN DIATOMS - MINERALIZATION OUTSIDE THE BOX?
2Department of Chemical Research Support, Weizmann Institute of Science, Rehovot, Israel
Diatoms are unicellular algae, abundant in all aquatic environments. The hallmark of diatoms is their mineralized cell wall, made of amorphous silica. The morphology of the cell wall is species-specific, forming distinct 3D micro- and nano-metric architectural features. The prevailing paradigm to explain the biological control over the formation of the inorganic phase is that each silica element is formed intracellularly inside a silica deposition vesicle (SDV), and once completed it is exocytosed. The complex cellular processes within the SDVs are thought to regulate the mineralization process.
Chaetoceros tenuissimus is a diatom species with a cell size of 5µm in diameter, which is characterized by four long extensions, called the setae, radiating from the main cell body. The setae are 15-30µm long and 250-300nm in diameter and are covered by a silica shell. Seta growth commences after cell division and continues at the seta tip until its full length is reached. Therefore, the growing tip of the C. tenuissimus seta is a unique system to study the cellular process of silica formation. We used cryo-TEM tomography to study the 3D structure of C. tenuissimus setae at various growth stages. Tomograms of seta tips were acquired using the 200kV Tecnai F20 and the 300kV Titan Krios microscopes. These tomograms clearly show the complex helical architecture of the thin silica fibers enveloping the seta. The cytoplasmic extension within the seta contained only a single microtubule filament inside the cell membrane. Importantly, none of the tomograms showed an SDV or other associated cellular structures at the tip of the setae. These results suggest a silicification mechanism in diatoms that is not SDV dependent, but rather a continuous process of extracellular silicification. This mechanism may explain other silica elements in diatoms and solve fundamentals unknowns about the biological process of silicification.
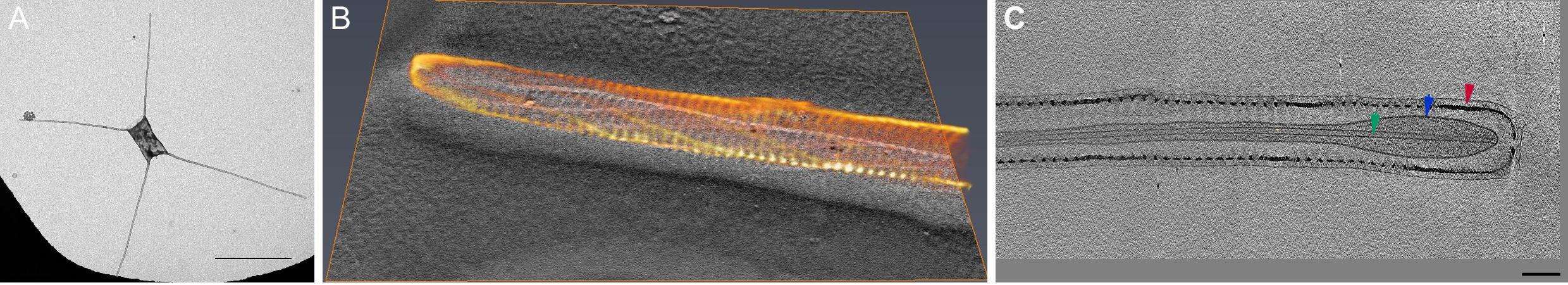
Figure: A) TEM image of C. tenuissimus, scale bar 10µm. B) 3D reconstruction of seta silica structure. C) TEM tomogram of internal structure of seta - red arrow marking silica cell wall, blue marking cytoplasm membrane and green marking microtubule, scale bar 100nm.
Powered by Eventact EMS