
Near-patient automated platform for rapid microfluidic extraction of circulating miRNAs from millilitre volumes of whole blood
2Division of Infection and Pathway Medicine, School of Medicine, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, UK
3Centre for Cardiovascular Science, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Midlothian, UK
4School of Biological Sciences, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, Midlothian, UK
Extracellular blood microRNAs (miRNAs) are promising clinical biomarkers but their measurement remains time-consuming, technically challenging and expensive. For circulating miRNA to have an impact on healthcare, a key challenge to overcome is the development of rapid and reliable low-cost sample preparation. There is an acknowledged issue with miRNA stability in the presence of haemolysis and platelet activation, and no demonstrated solution for fast and robust extraction at the site of blood draw. We demonstrate for the first time a microfluidic system able to perform the extraction of circulating miRNAs from several millilitres of whole blood in a single disposable cartridge, on a fully automated support, delivering a stable elution of miRNA in less than 45 minutes. The microfluidic platform is using a hydrodynamic plasma separation step and on-board reagents. This platform enables the standardisation of sample preparation at the point of blood draw and in resource limited settings and could aid the introduction of miRNA based assays into routine clinical practice.
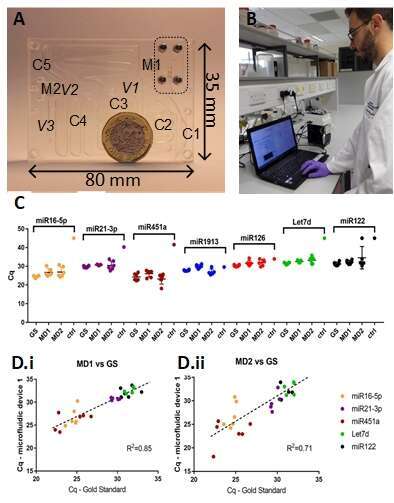
Figure 1: Circulating Nucleic Acid extraction cartridge (A) Photograph of the polymeric PMMA disposable cartridge. Outlined in dashed box is the blood plasma separation module (PMMA and SU8). (B) A user with the prototype controlled platform (control via laptop). (C) Direct comparison of miRNA extraction with cartridge MD1 and MD2, benchmarked against the gold standard bench protocol. Whole blood from 6 healthy volunteers were processed by the two microfluidic devices and compared to standard RNA extraction from the gold standard bench protocol (GS) (Data is expressed as the raw Cq values, mean ± SEM, n = 6)). As negative control (ctrl) we used deionised water. D) Correlation between Cqs obtained with microfluidic and bench extraction. Data points were not included in this analysis when qPCR duplicates showed Cqs differing more than 2 Cq or Within 2 Cqs from negative control.
Powered by Eventact EMS