
Spatial - temporal study of plasma-waves and ionospheric parameters using microsatellites.
2Department of Geophysical Electrodynamics, Applaid Physics Institute of the RAS, Nizhny Novgorod
3LEMI, Institute for Space Research of NAS and SSA of Ukraine, Lviv
4Department Geophysics and Space Sciences, Eötvös University, Budapest
5Geophysical, Geodetic and Geophysical Institute of HAS, Sopron
6Particles, Wigner Research Centre for Physics, HAS, Budapest
7BL, BL Electronics LTD., Budapest
The implementation of microsatellites (MS) Kolibri-2000 (2002) [1] and Chibis-M (2012-2014) [2] showed that the electromagnetic monitoring of the ionosphere can be successfully carried out with the help of MS that are integrated into the Infrastructure of the Russian segment of the International space station (ISS RS) and the release from the cargo ship Progress in autonomous orbit with altitude of 500-600 km.
The method of ionosphere research using (Fig. 1) simultaneously release two copies of MS Trabant (weight of each ~60 kg., 2020-2024) to study:
- mechanisms of occurrence and dynamics of ionosphere inhomogeneties of different scales depending on the active processes in the Sun and on the Earth - space weather;
- regularities of changes in plasma-wave and electromagnetic parameters in the ionosphere of natural and technogenic character in a wide dynamic and frequency ranges;
In the monitoring mode (time resolution of tens of seconds), long series of the same type of data reflecting the "correct" statistics of observations are recorded. High-frequency modes (wave form) are included in some parts of the orbit, creating the most effective diagnosis of events — this is the implementation of the idea of "case study", but the price for the high information content of this mode is the loss of the picture of phenomena as a whole.
Multiparameter plasma-wave studies on a wide range of ionosphere deterministic spatial parameters (~ 0.1-100 km) will be carried out in a bundle of two MS Trabants.
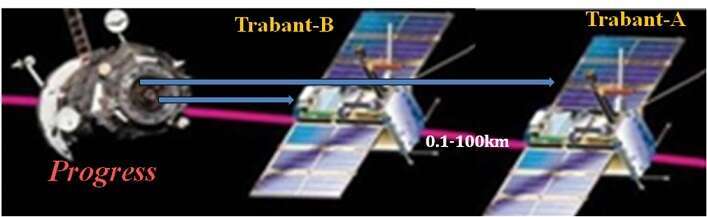
Fig. 1. The output circuit from the Progress of the Trabant-A and Trabant-B for autonomous orbits.
- Klimov, S.I., G.M. Tamkovich, et al. Aerospace education program realization by means of the micro-satellite. Acta Astronautica, Volume 56, Issues 1-2, January 2005, pp. 301-306, 2005.
- Zelenyi, L.M., A.V. Gurevich, S.I. Klimov, et al. Cosmic Research, 2014, Vol. 52, No. 2, pp. 87–98 DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.1.3811.1760.

Powered by Eventact EMS