
Neural activation threshold reduction using 3D micro-well electrodes: Towards a high resolution retinal prosthesis
2The Alexander Kofkin Faculty of Engineering, Bar-Ilan University, Ramat-Gan, Israel
3Bar-Ilan Institute for Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials (Bina), Bar-Ilan University, Ramat-Gan, Israel
Background: Electrical stimulation of the viable neurons in retinal degenerative diseases offers great hope for vision restoration. However, poor cell-electrode coupling, electrode size and density among others limit the currently provided visual acuity. Our novel Hybrid Retinal Implant (HRI) approach, based on a high-resolution electrode array integrated with glutamatergic neurons aims at overcoming the aforementioned limitations and achieving near-normal visual acuity by enhancing the cell-electrode coupling in 3D well structures, which confine the electrical field. Here we present the fabrication process of such a device and preliminary investigations of the concept.
Methods: The postulated electrical field confinement effect on the neural activation threshold was investigated by numerical modelling incorporated with biophysical neuron properties (COMSOL Multiphysics). Next, 1mm implant with gold electrodes in SU8 well-like scaffold was fabricated by optimized photolithography sequences as well as MEA (various well sizes) for in-vitro electrophysiological investigations and were characterized by profilometer measurements, and SEM/FIB imaging.
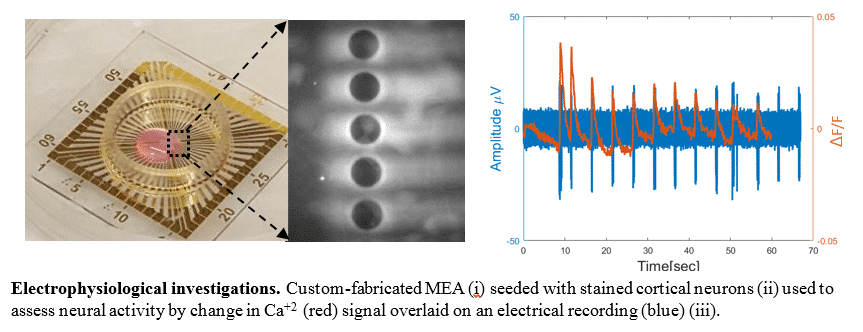
Cortical neurons were seeded on the MEAs and were electrically stimulated in four different modalities: Intracellularly, extracellularly (pipette in close proximity with the cells) and two MEAs types (planer and wells). The induced electrophysiological signals were then measured using either intracellular, extracellular recording combined with calcium imaging (OGB).
Results: Our preliminary results reveal that the electrical field confinement induced by the 3D well structures enabled the reduction of activation thresholds towards those of intracellular levels (pC levels). The enhanced coupling was further highlighted by the higher action potential amplitude observed by the extracellular recordings
Conclusion: Herein we presented the reduction of neural activation thresholds, using sealed 3D micro-well structures. These results lay a foundation for further studies for the realization of the HRI concept.
Powered by Eventact EMS