
Engineering new metal–organic framework for cooperative heterogeneous C-C bond formation
2School of Chemistry, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel
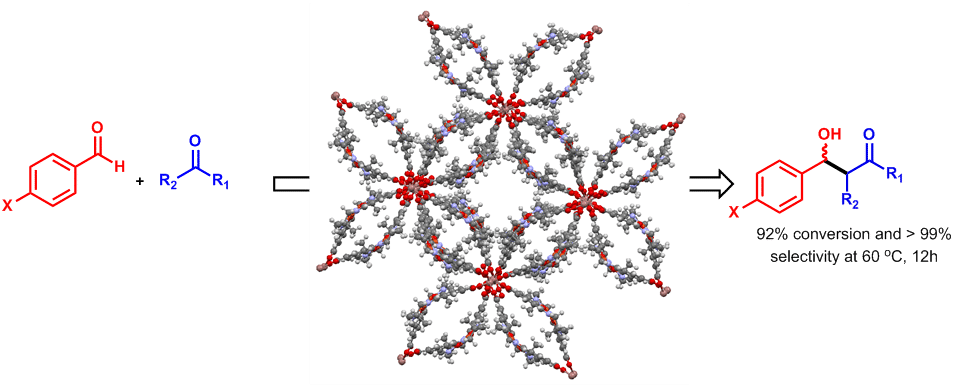
Currently, great interest is focused on developing cooperative heterogeneous catalytic reactions, in which substrates are transferred between the two active sites and enhance the reaction rate for achieving desired products. In this work, we demonstrate cooperative heterogeneous catalysis for the aldol reactions by a new bimetallic Cu (salen) based metal−organic framework (MOF) (TIF-1), which after post synthesis with sodium salts of carboxylates affords remarkably increased catalytic activity and selectivity (>92% conversion and >99% selectivity) as compared to the original metal−organic framework (TIF-1). This increased catalytic activity as a result of the Cu-amine units in close proximity within its open channels. The cooperative catalysis further evidenced by changing electron rich and electron poor carboxylate anions within the MOF pores. The effect of reaction parameters (reaction time, temperature, and substrate effect) on the catalytic performance was also investigated in detail. Furthermore, these MOF’s high porosity and large pores was explained by organic anionic dye absorption studies.
Powered by Eventact EMS