
Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Increases Drug Retention of Anti–Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha Agents in Pediatric Patients with Crohn’s Disease
Background: Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha (anti-TNFα) agents has been commonly utilized. We investigated its effect on drug retention and clinical outcomes in pediatric patients with Crohn`s disease (CD).
Methods: Medical records of pediatric CD patients receiving anti-TNFα agents from 2007 to 2018 were reviewed retrospectively. Patients were stratified to those who initiated anti-TNFα treatment between 2007 and 2012, an era when TDM was not available (TDM-), and patients who initiated anti-TNFα treatment between 2013 and 2018, with at least 1 TDM during firstline anti-TNFα treatment (TDM+). Main outcome measures included time to first anti-TNFα discontinuation (drug retention) and flare, hospitalizations per year of first anti-TNFα treatment, treatment intensification rate and surgical resection rate.
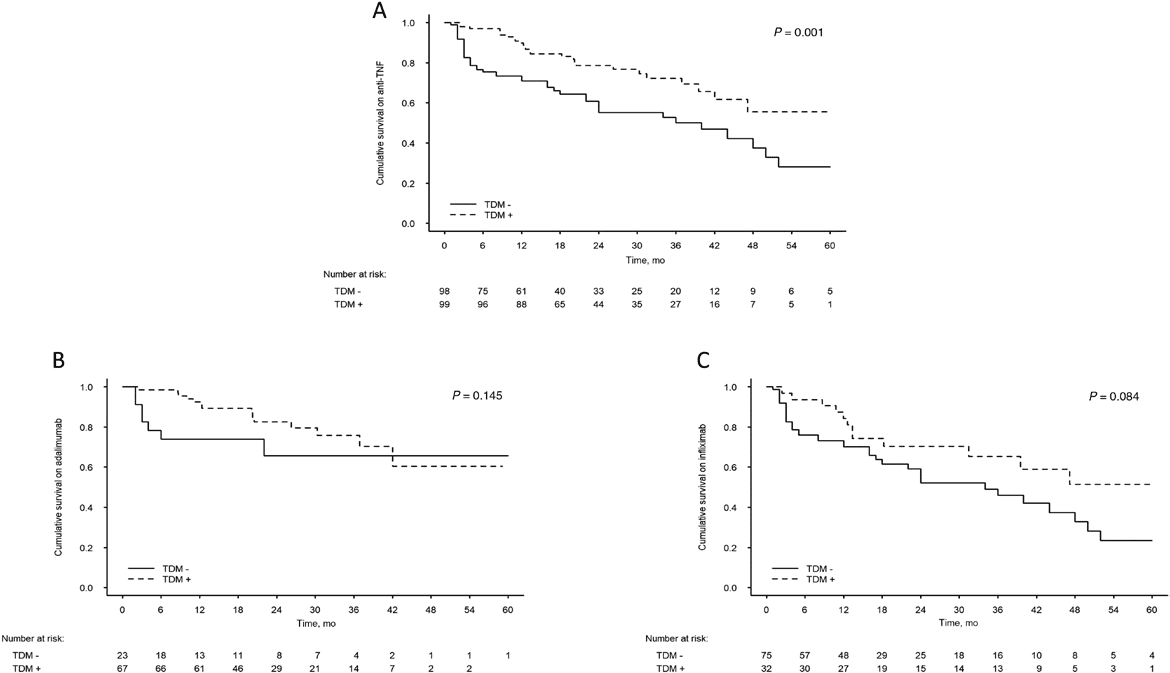
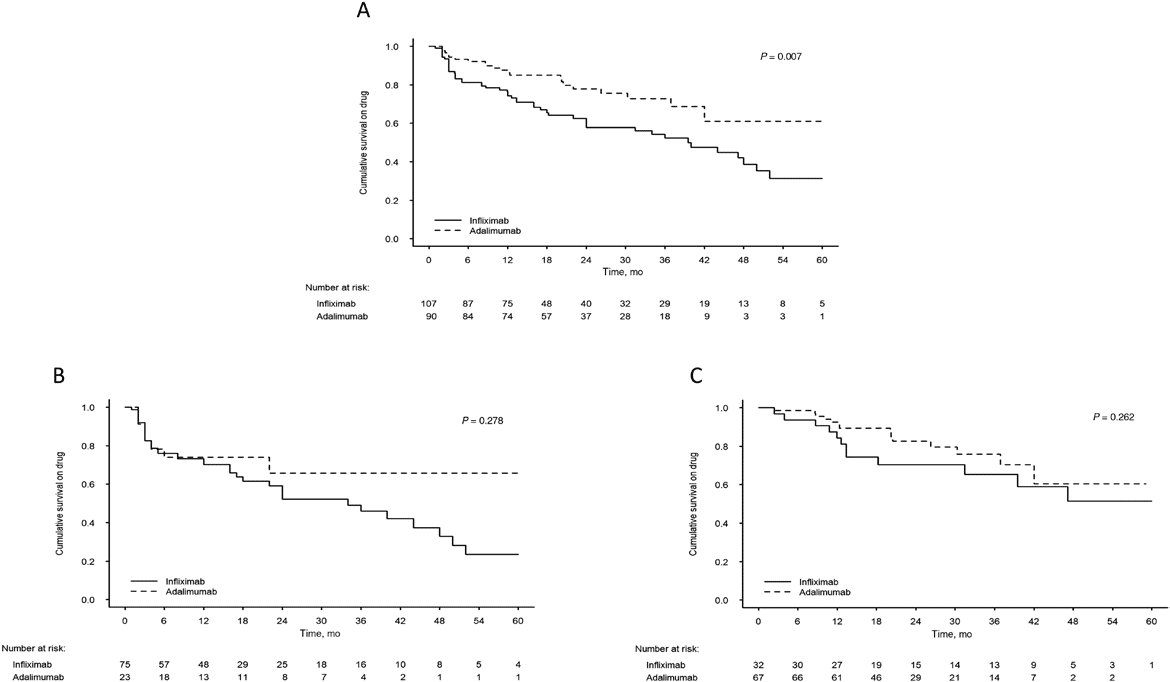
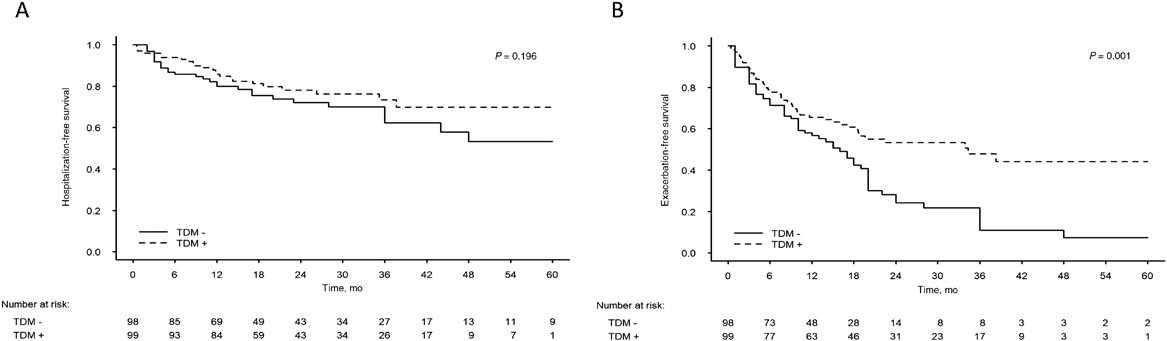
Results: 197 patients were included (n = 98, TDM-; n = 99, TDM+; median [interquartile range] age, 12.6 [10.1-14.2] years; females 68 [35%]). Compared with the TDM- group, the TDM+ group had a longer drug retention time (mean ± SE, 45.0 ± 2.7 vs 33.5 ± 2.4 months; P = 0.001), lower hospitalization rate per patient per year (mean ± SE, 0.51 ± 0.7 vs 0.92 ± 0.81; P < 0.001), and higher treatment intensification rate (70% vs 18%; P < 0.001). Surgical resection rate was not significantly different. Analysis of the entire cohort showed longer retention time for adalimumab vs infliximab (45.3 ± 2.8 vs 34.8 ± 2.5 months; P = 0.007).
Conclusions: TDM-based treatment enables longer drug retention time, reflecting better utilization of anti-TNFα agents, with several additional favorable outcomes.
Powered by Eventact EMS