
Tandem Iridium catalyzed alkene isomerization-Cope rearrangement of epoxides for the diastereoselective synthesis of acyclic 1,6-dicarbonyls
Schulich Faculty of Chemistry, Technion – Israel Institute of Technology, Haifa, Israel
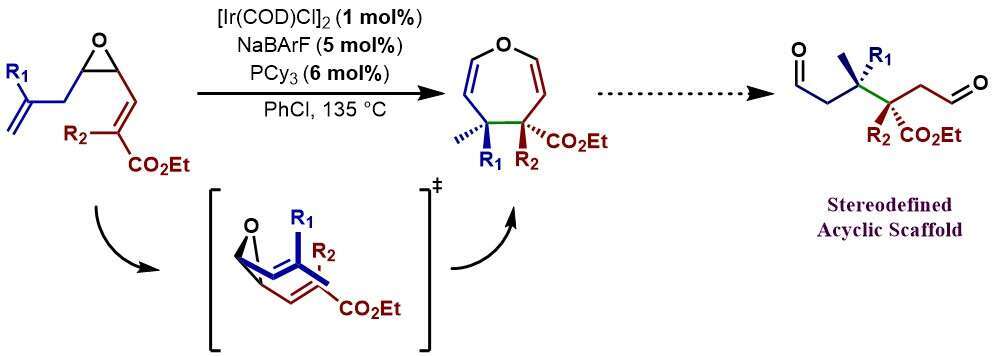
The Cope rearrangement of divinyl epoxides is a rare example of C-C bond cleavage in an epoxide. The resulting 4,5-dihydrooxepines are amenable to hydrolysis, furnishing 1,6 bis-aldehydes with two contiguous stereocenters in the 3 and 4 positions, which are highly challenging to access stereoselectively through classical methods. We use a cationic Iridium-based catalytic system for the stereoselective alkene isomerization of an allyl epoxide to form the reactive 2,3-Divinyloxirane. These intermediates subsequently undergo a [3,3] oxy-Cope rearrangement in-situ, to generate 4,5-dihydrooxepines with complete stereocontrol and high yield.
Powered by Eventact EMS