
Visible solar light mediated benzylic C-H oxygenation
Department of Chemical Sciences, Ariel University, Ariel, Israel
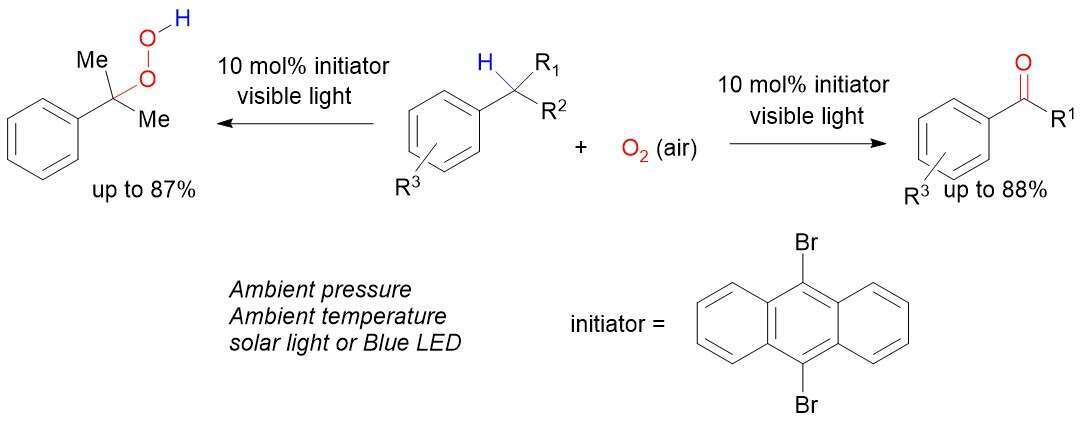 This poster presents a novel visible light mediated benzylic C-H oxygenation reaction. The reaction is initiated by solar light and uses 9,10-dibromo-anthracene as an initiator and source of bromine radicals. Secondary benzylic positions are oxygenated to ketones while tertiary benzylic C-H bonds are oxygenated to give hydroperoxides. Atmospheric air serves as the source of oxygen. Notably cumene hydroperoxide is produced in higher yield and at milder conditions than the currently employed industrial conditions. This process could significantly reduce energy and infrastructure cost in the million ton per year production of phenol from cumene hydroperoxide.
This poster presents a novel visible light mediated benzylic C-H oxygenation reaction. The reaction is initiated by solar light and uses 9,10-dibromo-anthracene as an initiator and source of bromine radicals. Secondary benzylic positions are oxygenated to ketones while tertiary benzylic C-H bonds are oxygenated to give hydroperoxides. Atmospheric air serves as the source of oxygen. Notably cumene hydroperoxide is produced in higher yield and at milder conditions than the currently employed industrial conditions. This process could significantly reduce energy and infrastructure cost in the million ton per year production of phenol from cumene hydroperoxide.
Powered by Eventact EMS