
1,2-dibenzoyl ortho-carborane a strong electron acceptor
O-carboranes are the most studied among the carboranes due to their high stability and
electron accepting properties.1 Unique electron-acceptor properties of the o-carborane
results from the delocalized σ-electron systems (‘3D aromaticity’). Due to these
properties, o-carborane plays an active role as strong electron withdrawing substituents
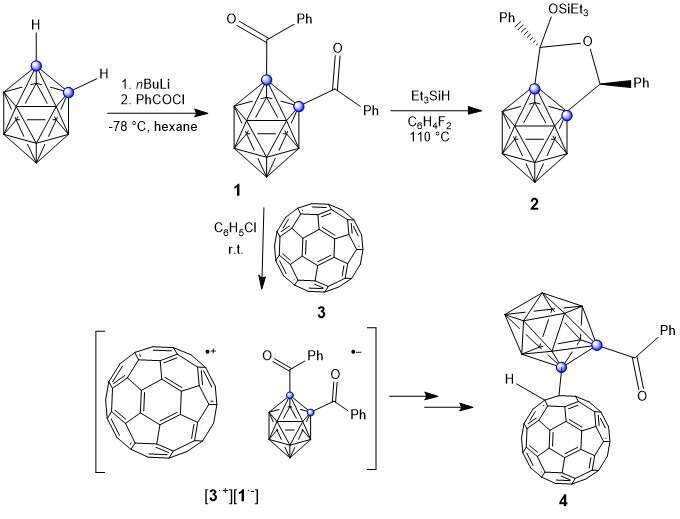
when connected through carbon atoms.2 Here, we have synthesized 1,2-dibenzoyl ocarborane
(1) (Scheme 1) and studied its reactivity. Reaction of 1 with one equivalent of
Et3SiH at 110 0C gave the product 2 (Scheme 1). To further study the electron acceptor
properties of 1, we carried out the reaction with [60]-fullerene (3) led to formation of 3•+
(Observed in EPR spectroscopy) and gave the product 4 (Scheme 1). Compound 4 was
characterized by mass spectrometry.
Scheme 1. Synthesis of 1,2-dibenzoyl o-carborane and reactivity study with Et3SiH and
fullerene.
References
1. Grimes, R. N. Carboranes, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2011.
2. Popescu, A. R.; Teixidor, F.; Vinas, C. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 269, 54-84.
Powered by Eventact EMS